
Chad Travel Safety
Travel Safety in Chad
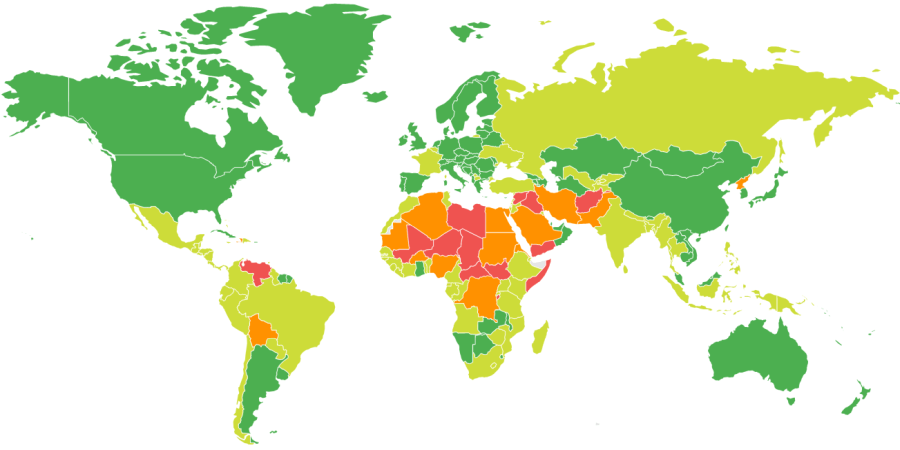
General travel safety in Chad on a scale of 1 to 4 — where 1 is safe and 4 is dangerous. Data compiled on the basis of Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs.
Country
Chad
Updates
Updated: 26 Jun 2025 • Still current at: 2 Jul 2025
Status
LEVEL 3 - Reconsider your need to travel (with regional exceptions)
There are serious and potentially life-threatening risks. This could be due to: an ongoing threat of terrorism or kidnapping, frequent incidents of violent crime, ongoing civil unrest, widespread disease or other safety risks. This can make the destination unsafe for tourism and unsuitable for most travellers. Think seriously about your need to travel to these places - this may mean postponing non-essential travel, or choosing a less risky destination.
Safety and Security Tips
Road safety
Road conditions are dangerous. Roads are poorly maintained and mostly unpaved, even in N'Djamena. Streets are poorly lit and road signs are often missing. Excessive speeds, erratic driving habits, lack of vehicle maintenance, roaming wildlife and livestock, cyclists and pedestrians pose risks. You are advised not to travel between cities at night due to poor road infrastructure. Fuel is not always available in major cities and is very scarce in rural areas. You should travel in a convoy outside N'Djamena, travel during daylight hours only and carry additional fuel, a spare tire and provisions. Keep windows closed and doors locked at all times. You should stop and cooperate at all police or military roadblocks. Proper identification should be readily available. It is preferable to hire a local driver to avoid being the victim of mob justice in response to a road accident.
Public transportation
There is no operational train or bus network in Chad. Trucks and minibuses are not properly maintained and are often dangerous - they are not recommended for any intercity travel.
Women's safety
Based on the crime situation of the Chad, incidents of attacks and sexual assault against foreign women, including rape and murder might occur. Be extremely vigilant at isolated places and while dealing with strangers. Avoid dark or non-tourist areas at night. Instead try to be around larger crowds, whether they are fellow tourists or local citizens. Female visitors and residents should take care when walking or travelling alone even during daylight hours. Exercise a very high degree of caution during travel.
Crime
Petty crime, such as pickpocketing and purse-snatching, occurs in markets and commercial areas. Banditry, burglary and vehicle theft are common. There has been an increase in armed robberies in N'Djamena in 2017, often in the vicinity of restaurants. In some cases, foreigners were targeted and injured. Do not show signs of affluence. Leave valuables and personal belongings, including cash and airline tickets, in a hotel safe or other secure place. Dress conservatively. Avoid walking alone, especially after dark. If confronted by an armed individual, do not resist.
Update 1 November 2020Emergency Calls
- Police17
- Fire18
- Ambulance2251-4242 or 2251-1237
Embassy of us
American Embassy in N'Djamena
AddressChagoua Round Point
Local Law and Culture
LGBT
Homosexuality is not widely accepted in central African society. In August 2017 a new law came into force criminalising same-sex sexual activity in Chad, with penalties of imprisonment ranging from 3 months to 2 years and a fine of between 50,000 and 500,000 CFA francs.
Illegal or restricted activities
Criminal convictions for possession or trafficking of drugs can result in strict penalties and often lengthy prison sentences. Persons violating Chad's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested or imprisoned. Convicted offenders may expect jail sentences and fines. You are required to have a government permit for all photography. It is prohibited to photograph airports, military establishments and government buildings. Film and cameras may be confiscated without notice. Conditions in local prisons are harsh.
Driving
An International Driving Permit is required.
Update 1 November 2020Vaccinations and Medications
A doctor's consultation is required prior to any vaccinations being administered. This section is for informational purposes and does not exhaust all issues related to vaccination. Please contact your doctor for complete information on this subject.
Stay Healthy and Safe
Act in advance of to prevent. Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least 4-8 weeks before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need.
All travelers
You should be up to date on routine vaccinations while traveling to any destination. Some vaccinations may also be required in Chad.
Before each trip, it is worth making sure that we are up to date with the routine vaccinations. These include vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, chickenpox, polio and flu.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Most travelers
Get travel vaccines and medicines because there is a risk of these diseases in the country you are visiting.
Hepatitis A is a digestive disease caused by the hepatitis A virus and is closely related to a lack of good hygiene.
It can be asymptomatic, moderate, or very severe.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Take antimalarial meds
- Prevent bug bites
Estimated relative risk of malaria in Chad
Wysokie
Areas with malaria
All
Typhoid fever is an acute, systemic infectious disease caused by Salmonella typhi.
The source of the infection may include dirty water, raw fruits, vegetables, dairy products, as well as dirt containing bacteria.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Some travelers
Vaccinations and medications that may be recommended under certain conditions, depending on where you will be, the length of your stay and the nature of your stay.
Cholera is a disease of the digestive tract caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
The most common infection occurs through the ingestion, mainly through water contaminated with human faeces, and also through food (mainly fruit, seafood). Less often by contact with the sick person and their environment.
Prevention
- Eat and drink safely
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Infection occurs through contact of injured skin or mucous membranes with virus-infected blood or other secretions (e.g. during sexual contact, through contaminated needles or as a result of medical procedures).
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Avoid sharing body fluids
- Avoid non-sterile medical or cosmetic equipment
Meningococcal disease is any illness caused by a type of bacteria called Neisseria meningitidis.
Infection occurs through droplets - through contact with the secretion of the patient or the host, e.g. when coughing, sneezing, kissing or sharing cutlery or dishes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Polio (Poliomyelitis), or Heine-Medina disease, is an acute infectious viral disease.
The infection occurs mainly through the ingestion or inhalation.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by neurotrophic viruses from the rhabdovirus family.
The infection is most often caused by biting a sick animal or other contact of its saliva with mucous membranes, conjunctiva or damaged skin.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Keep away from animals
Yellow fever is an acute viral disease which is transmitted by virus-infected mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Prevent bug bites
Vaccination requirements
Required if traveling from a country with risk of YFV transmission.
We have made every effort to ensure that the information presented reliably reflects the general safety situation in a given place. However, the data is provided for informational purposes only and we do not take responsibility for any damages or losses resulting from incorrect risk assessment. Before each trip, we recommend checking the current situation in the country of destination on the websites of the relevant Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 Libya
Libya