San Miguel Volcano

Facts and practical information
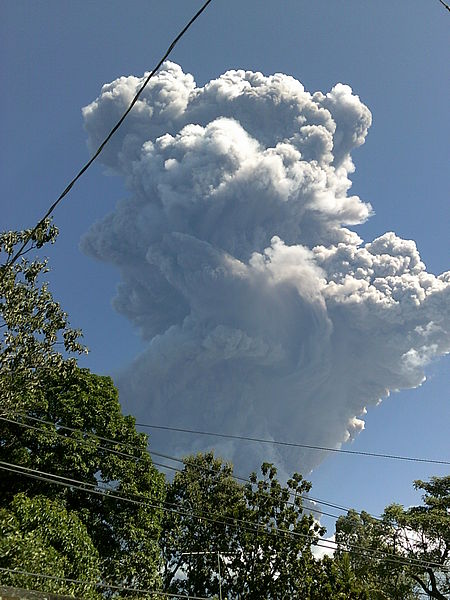
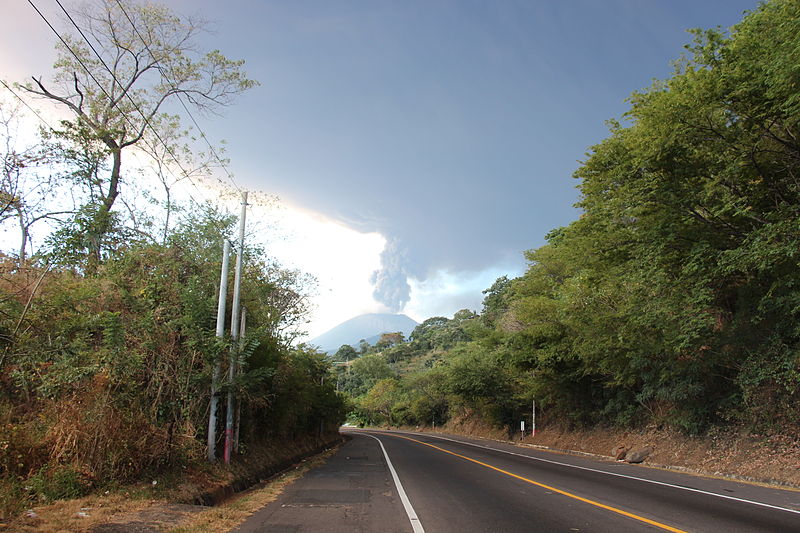
San Miguel Volcano, also known as Chaparrastique, stands as an imposing natural landmark in eastern El Salvador. This stratovolcano, reaching an altitude of 2,130 meters, is one of the most active in the country, with its last major eruption occurring in December 2013.
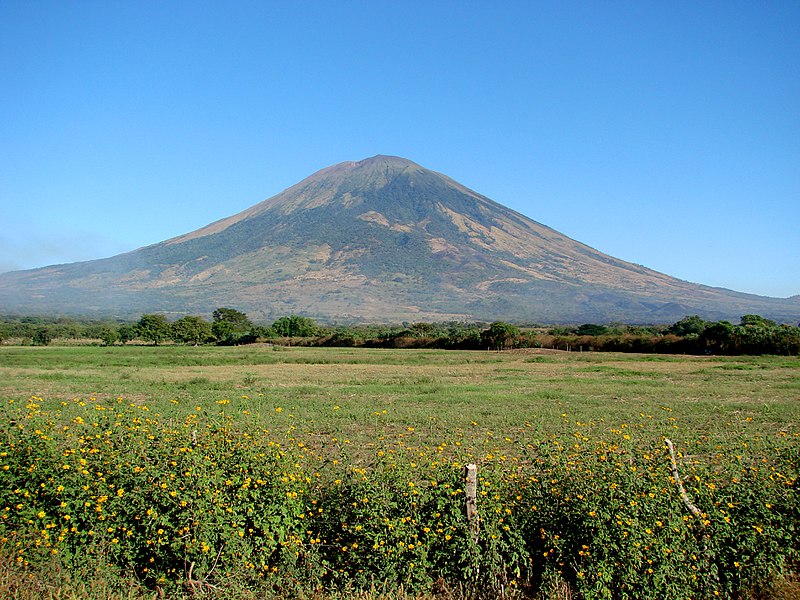
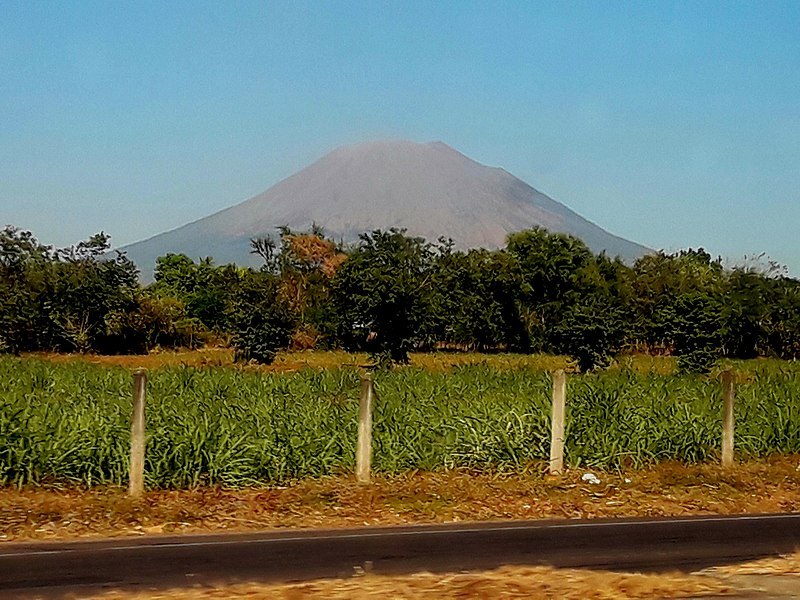
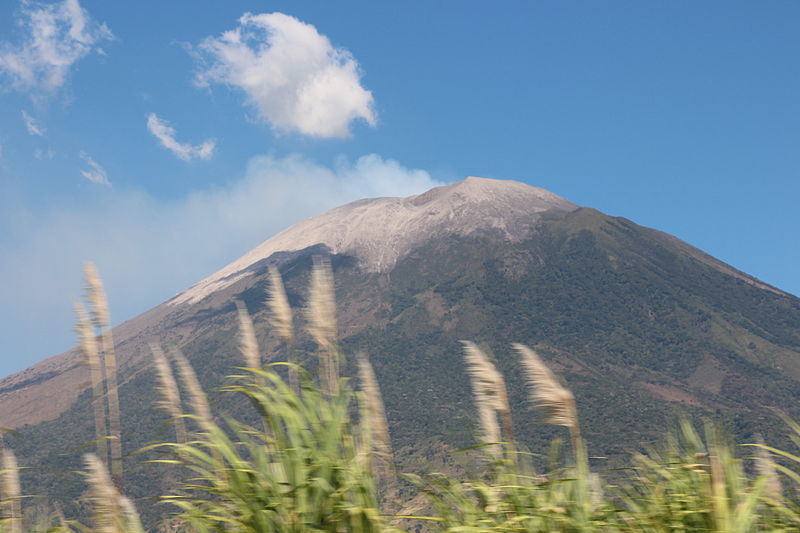
San Miguel Volcano's symmetrical cone, which is visible from far distances, dominates the surrounding landscape and is a prominent feature of the region. Its slopes are marked by deep ravines and covered with coffee plantations and other forms of agriculture, benefiting from the fertile volcanic soil.
The volcano has a history of frequent, though generally small eruptions, with a record of activity dating back to the 17th century. The local population is well aware of the potential hazards, and contingency plans are in place in case of future eruptions.
Despite the inherent risks, San Miguel Volcano is a popular spot for adventurous tourists and hikers. The ascent to the summit offers stunning views of the crater and the surrounding landscape, including the Pacific Ocean. However, due to the active nature of the volcano, visitors are advised to check current conditions and potential volcanic activity before planning their climb.
San Miguel Volcano – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Chinameca Volcano.