Hekla

Facts and practical information
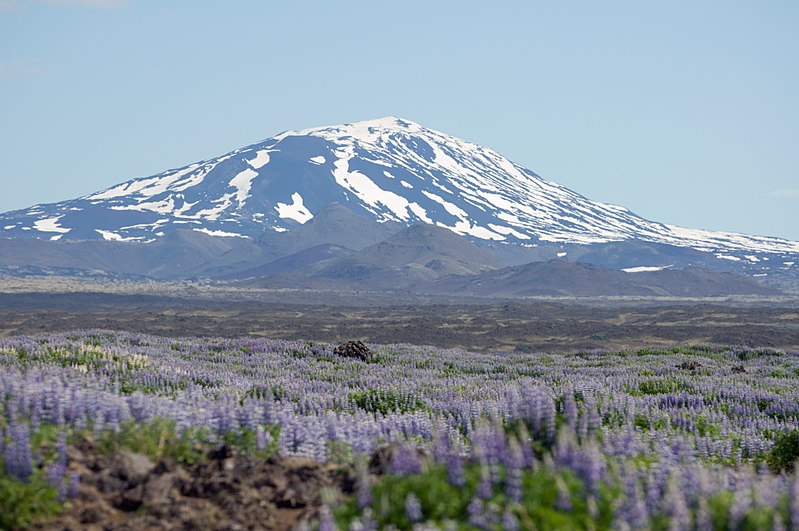
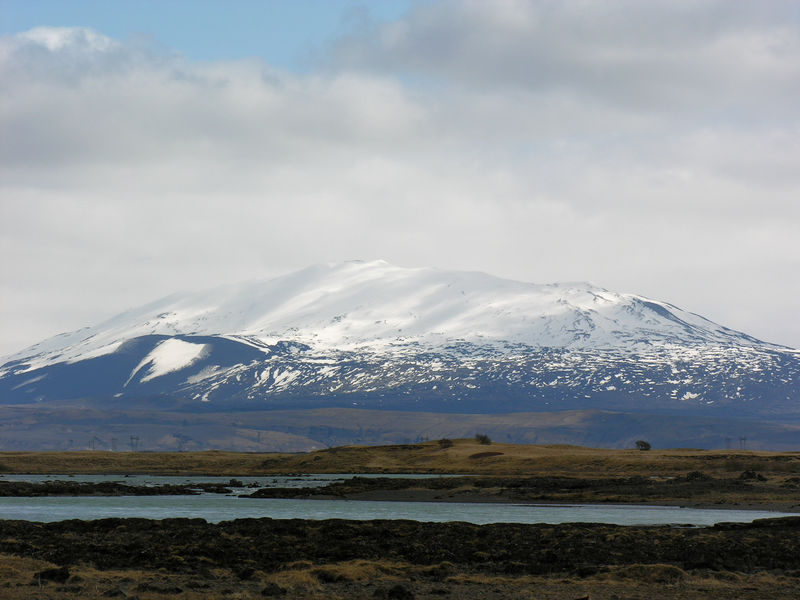
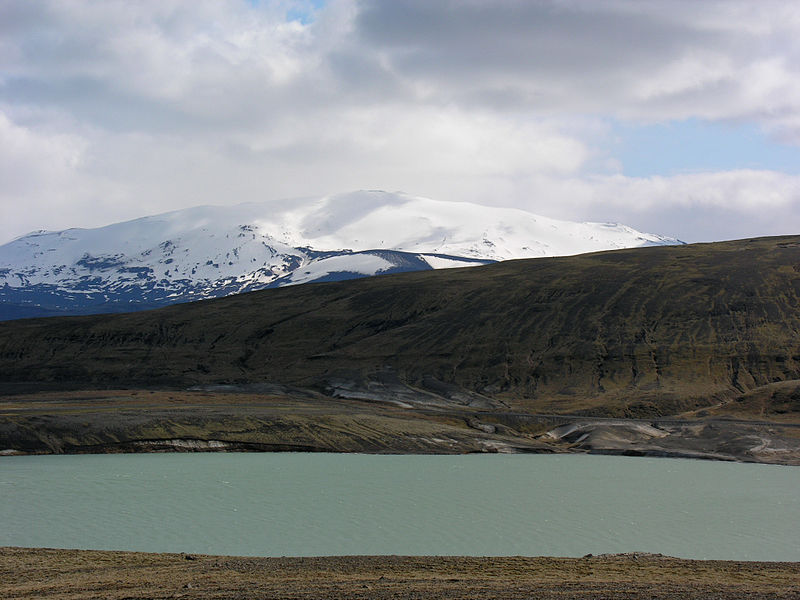
Hekla, one of Iceland's most active and renowned volcanoes, stands as a majestic and formidable natural structure on the island's south-central region. Towering approximately 1,491 meters above sea level, Hekla has earned the moniker "Gateway to Hell" throughout the centuries, owing to its frequent and explosive eruptions.
The volcano has a history of eruptions that dates back to 1104, with over 20 significant occurrences since the settlement of Iceland. Its most recent activity was recorded in the year 2000, marking Hekla as a volcano of significant interest to both volcanologists and tourists alike.
Hekla's silhouette is an iconic feature of the Icelandic landscape, characterized by a long, narrow fissure that runs about 5.5 kilometers along its summit, giving it a distinctive appearance compared to other volcanic structures. The surrounding area is marked by lava fields and ash deposits, bearing witness to the volcano's power to reshape the environment.
Visitors to Hekla can engage in a variety of activities, including hiking, with several trails leading to its slopes. However, due to the potential dangers associated with its unpredictable nature, it is advised to take caution and check for any warnings or activity updates before attempting a climb.
Hekla – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Vatnafjöll.