Dur-Kurigalzu, Baghdad

Facts and practical information
Nestled within the historical tapestry of Iraq, Dur-Kurigalzu stands as a testament to the ancient world's architectural prowess and cultural depth. Located near the modern city of Baghdad, this archaeological site offers a window into the past, specifically to the Kassite period of Mesopotamian history.
Founded by the Kassite king Kurigalzu I in the 14th century BCE, Dur-Kurigalzu, which translates to "the fortress of Kurigalzu," served as a political and religious center. The site is primarily known for its well-preserved ziggurat, a massive terraced structure that was central to the city's religious life. The ziggurat's core, made of sun-dried mud-brick and faced with fired bricks, has withstood the test of time, remaining as one of the key features of this ancient city.
The city itself was constructed strategically, with a fortified area containing palaces and temples, including the ziggurat, while the outer city housed residential quarters. Although much of Dur-Kurigalzu lies unexcavated, the discoveries made so far have provided valuable insights into the urban planning and construction techniques of the Kassites.
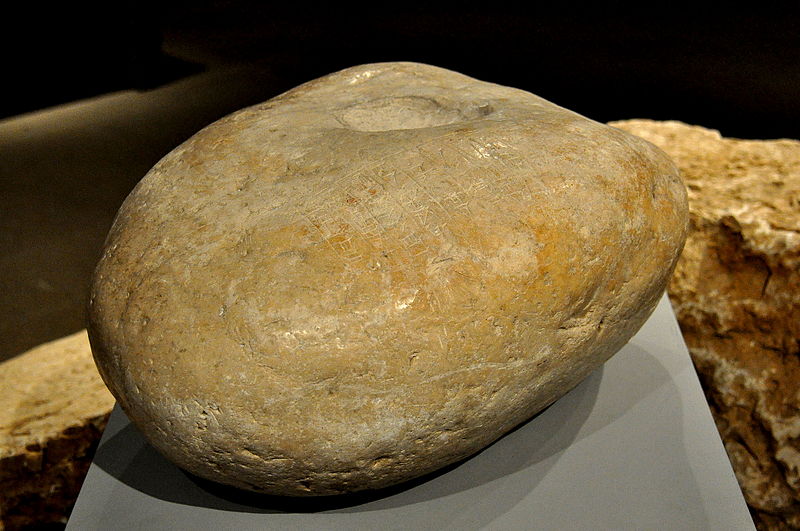
Excavations have also unearthed a variety of artifacts, including Kassite cuneiform tablets that offer a glimpse into the administrative and economic aspects of the city. These finds have contributed significantly to our understanding of the Kassite dynasty, which ruled over Babylonia for several centuries, leaving an indelible mark on the region's history.
Dur-Kurigalzu – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Al-Faw Palace, Umm al-Qura Mosque, Al-A'amiriya, Al-Jihad.