Ignatievka Cave

Facts and practical information
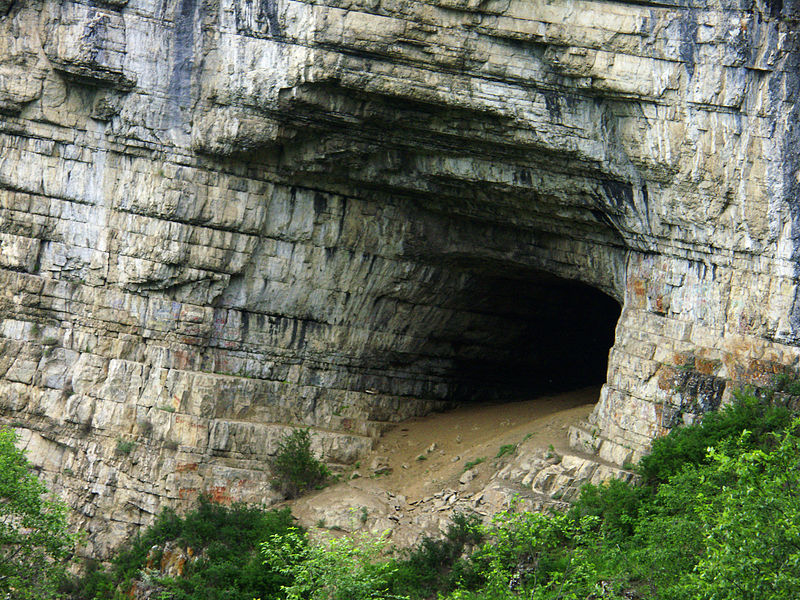
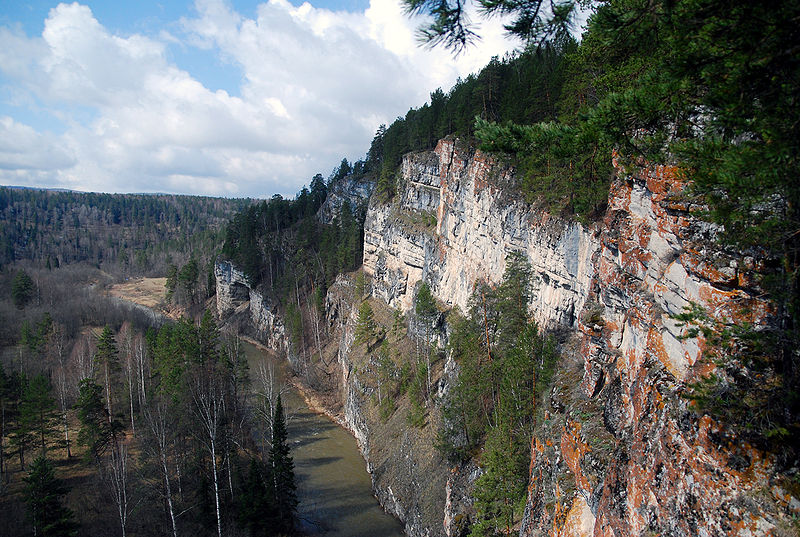
Ignatievka Cave, located in the Ural Mountains of Russia, is a prehistoric site that has captivated archaeologists and paleontologists for decades. This natural limestone formation, known for its impressive size and historical significance, has provided a window into the lives of ancient humans and animals who once inhabited the region.
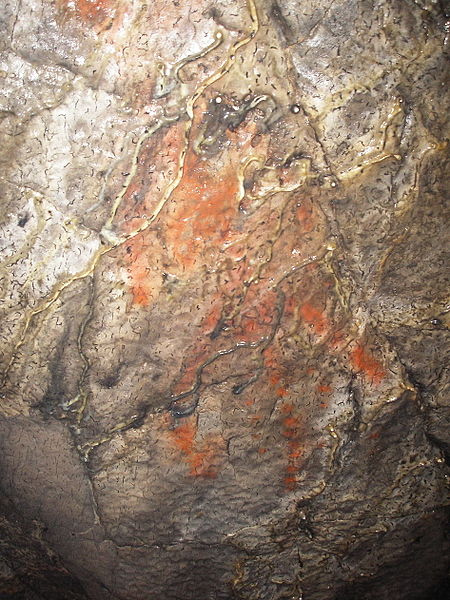
The cave's interior is adorned with a range of Paleolithic art, including drawings and engravings that depict various animal species, some of which are now extinct. These artworks are believed to be over 15,000 years old, offering a glimpse into the creative expression and cultural practices of prehistoric communities.
Beyond its artistic treasures, Ignatievka Cave has yielded numerous archaeological findings, such as tools, ornaments, and human remains. These artifacts have been instrumental in understanding the daily lives, survival strategies, and social structures of the cave's ancient occupants. The presence of human fossils has provided valuable information on the physical characteristics and health of these early humans.
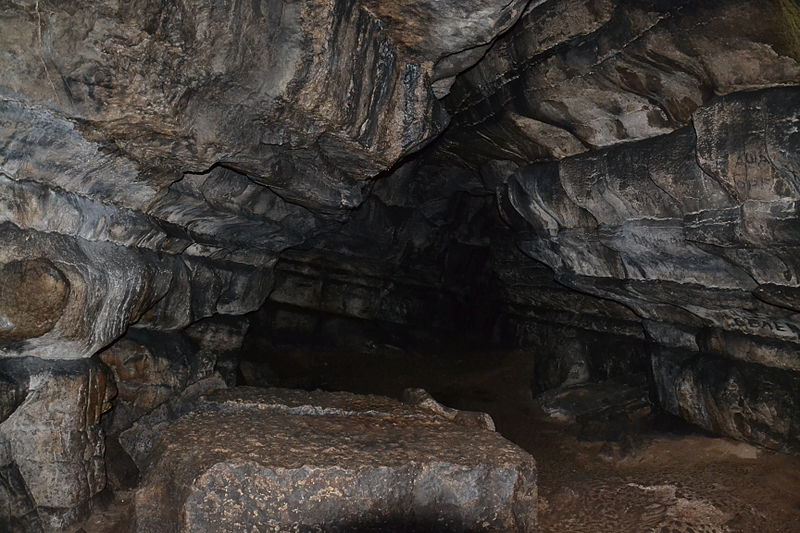
The cave's structure is also of geological interest, with its spacious chambers and narrow passageways revealing the natural processes that have shaped the cave over millennia. Speleologists study the cave's formations, including stalactites and stalagmites, to learn more about the region's geological history.
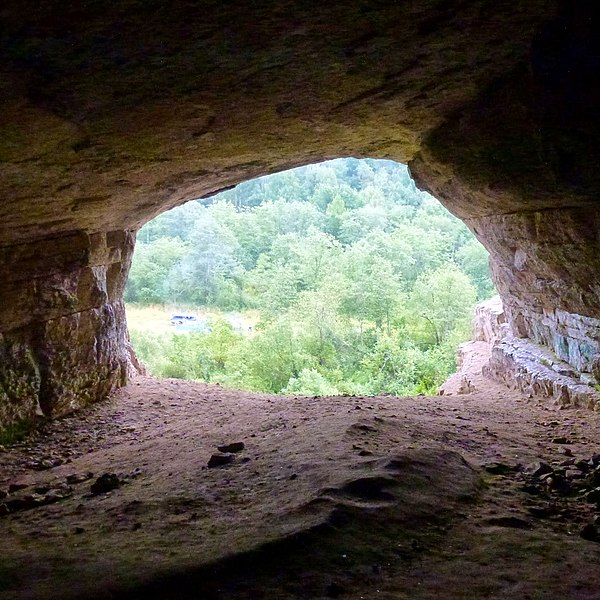
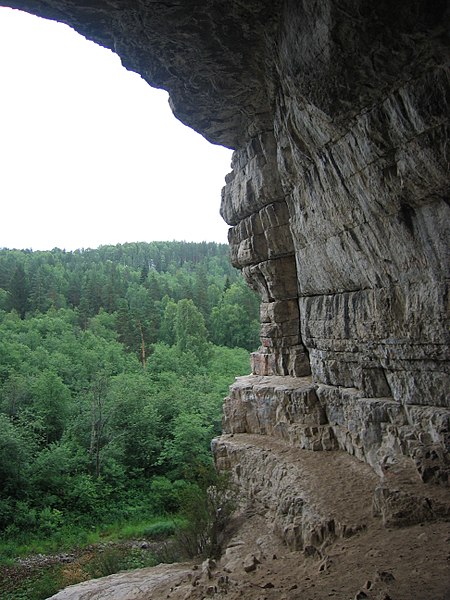
Ignatievka Cave is not only a site of scientific importance but also a place of natural beauty that attracts tourists and caving enthusiasts. Its remote location and the rugged terrain of the Ural Mountains add to the sense of adventure for those who visit.
Chelyabinsk