Licancabur

Facts and practical information
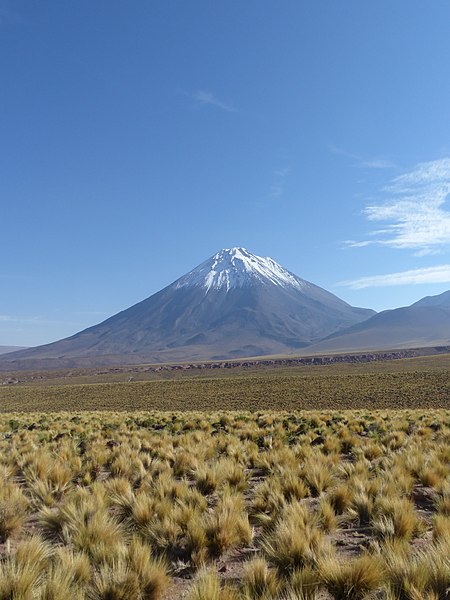
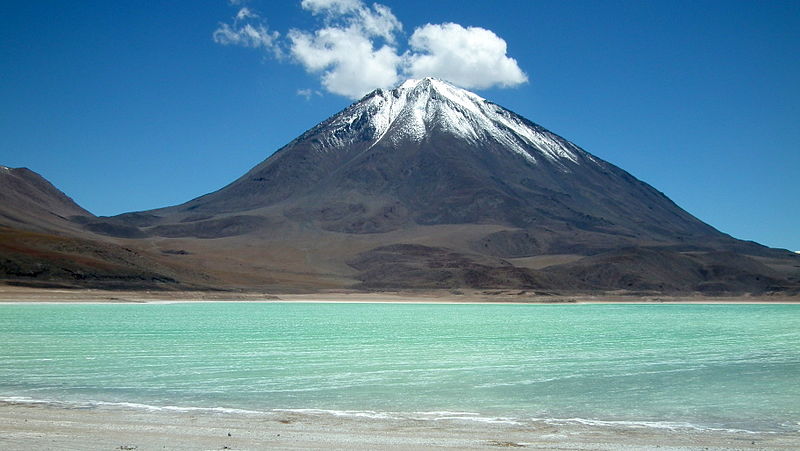
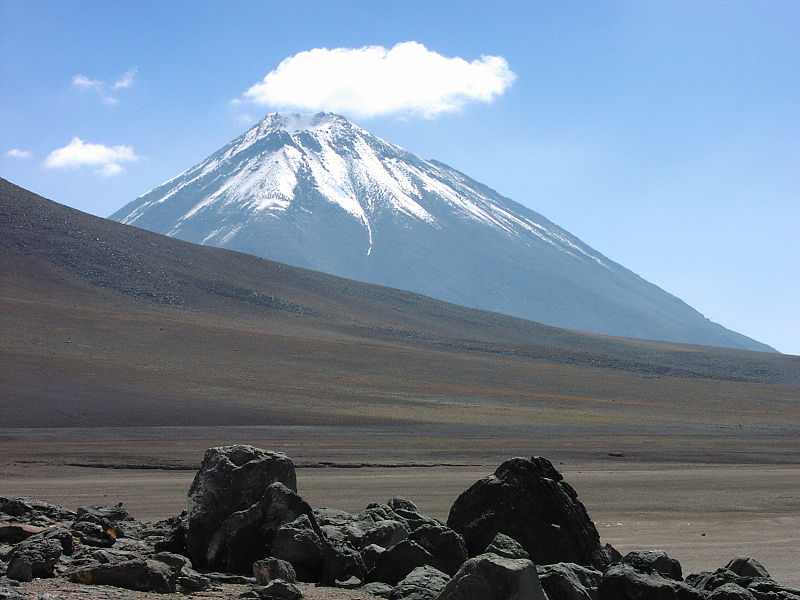
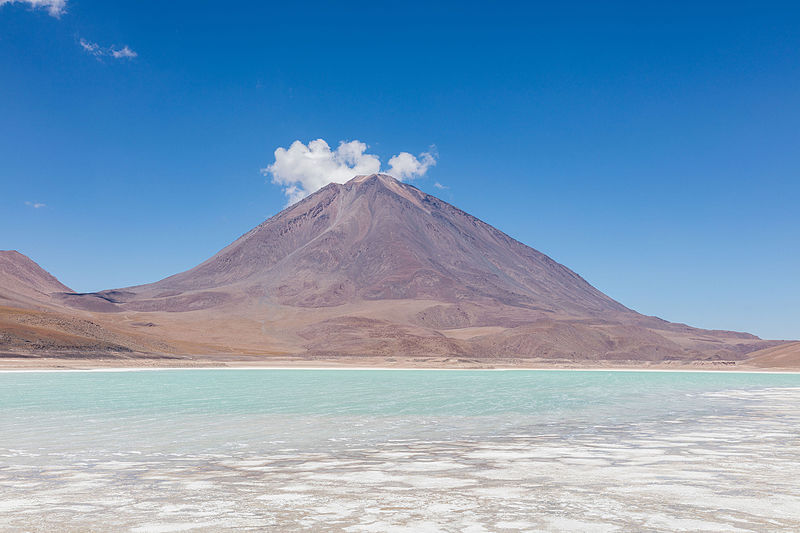
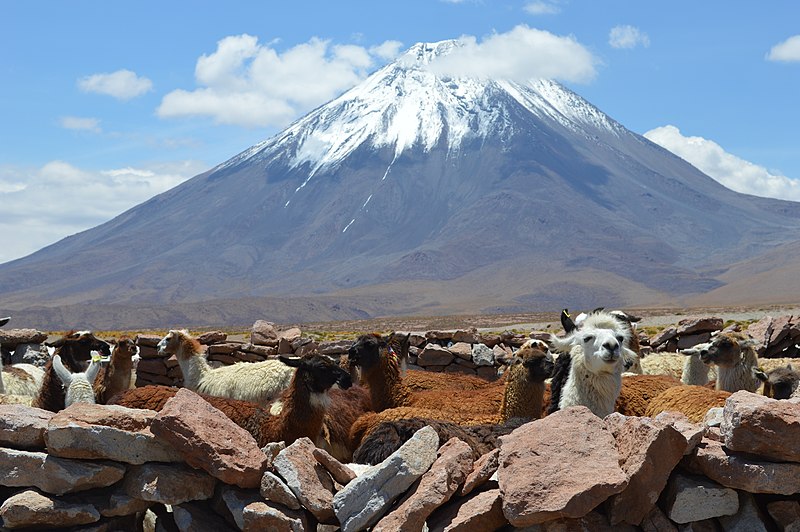
Licancabur is a striking volcano that dominates the landscape on the border between Bolivia and Chile. Standing at an impressive altitude of 5,920 meters (19,420 feet), Licancabur is part of the Andean Volcanic Belt and is one of the most iconic natural landmarks in the region.
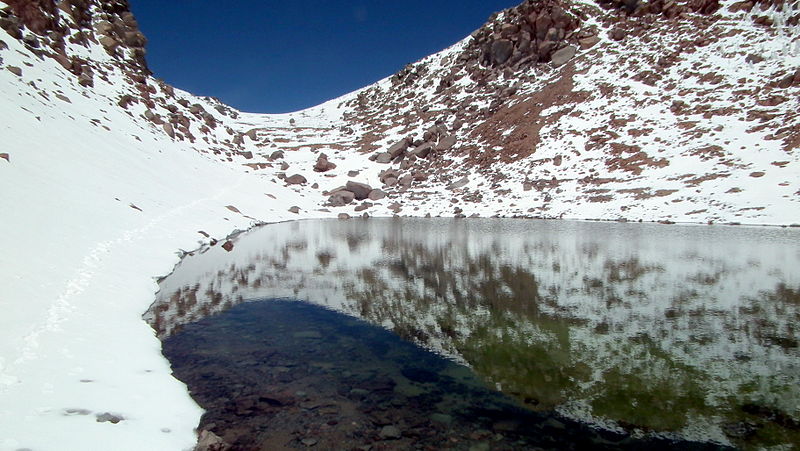
This symmetrical, conical volcano is not only a geological wonder but also a site of historical and cultural significance. Its name means "the people's mountain" in the Kunza language, reflecting its importance to the indigenous Atacameño people. The volcano's almost perfect shape and the clear blue lake in its crater, which is one of the highest lakes in the world, add to its mystique and beauty.
Despite its high altitude and remote location, Licancabur attracts adventurous travelers and mountaineers from around the globe. The ascent to the summit is considered a challenging hike, requiring acclimatization to the high altitude and often conducted as part of a guided tour. Those who reach the top are rewarded with stunning panoramic views of the surrounding desert landscape and the adjacent Salar de Atacama, one of the largest salt flats in the world.
Licancabur is not just a destination for thrill-seekers; it is also of interest to scientists. Due to the extreme conditions at its summit, researchers study the crater lake and surrounding environment to understand life in extreme habitats and to draw parallels with similar conditions that might be found on Mars.
Potosí
Licancabur – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Juriques, Laguna Verde, Laguna Verde.