Zhoukoudian, Beijing

Facts and practical information
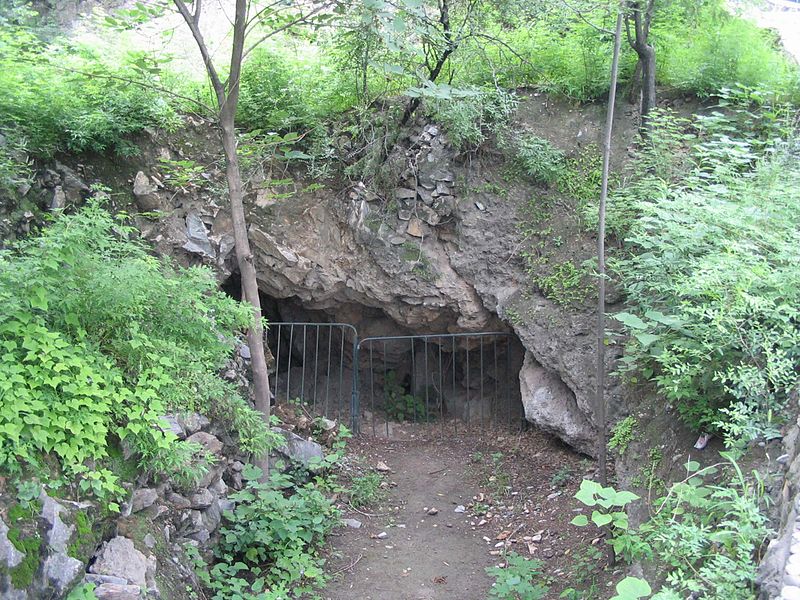
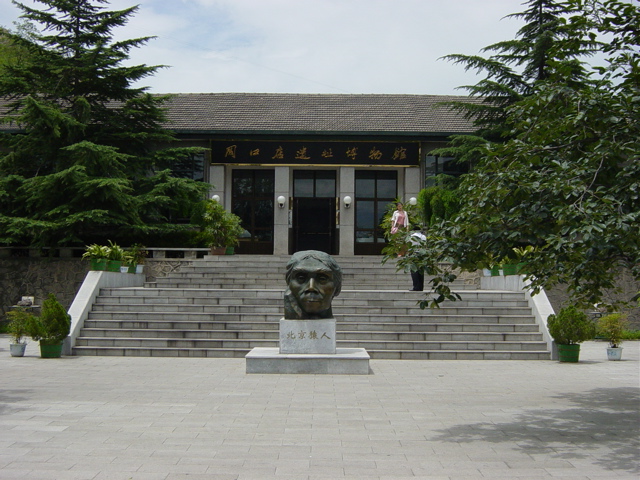
Zhoukoudian, situated on the outskirts of Beijing, China, is a site of great paleoanthropological significance, renowned for the discovery of the hominid fossils known as 'Peking Man'. This UNESCO World Heritage site is not just an excavation area but also a museum, offering a fascinating glimpse into prehistoric life.
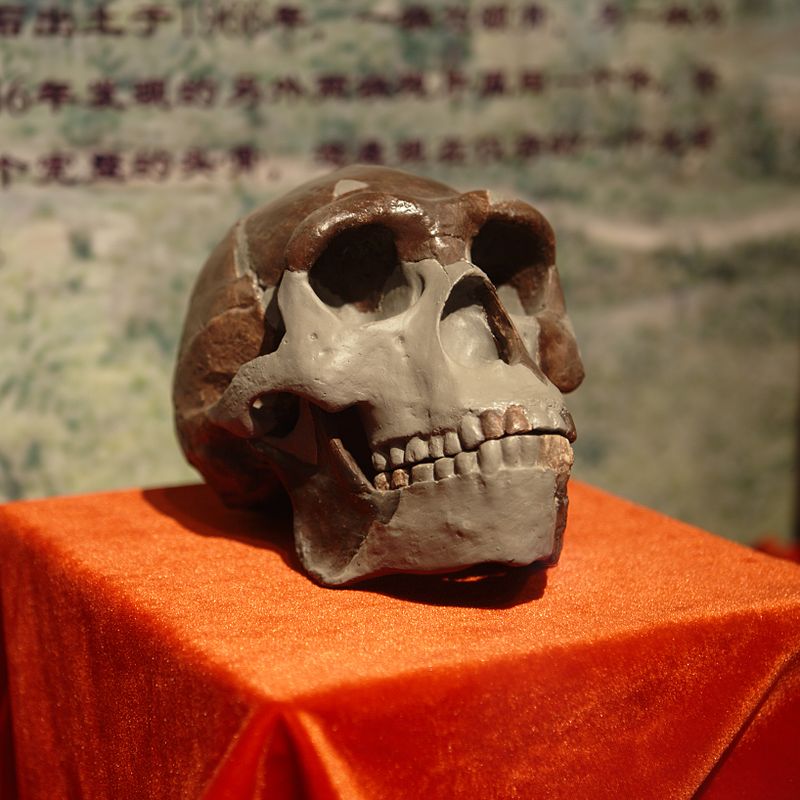
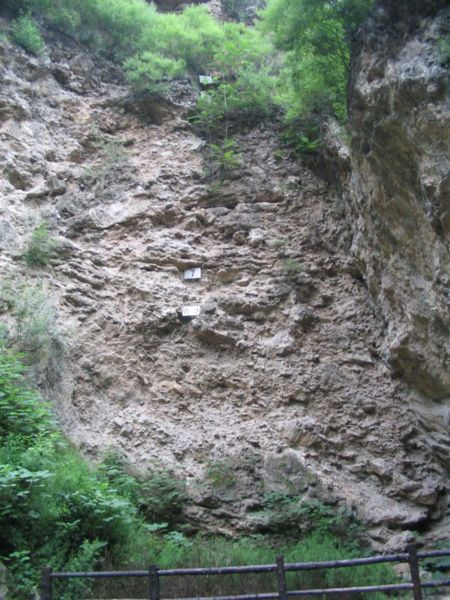
The site gained international prominence in the early 20th century when the remains of Homo erectus pekinensis, dating back some 750,000 years, were unearthed, providing invaluable insight into the evolution of humans. Zhoukoudian has since been a hotbed for archaeological research, yielding numerous other ancient artifacts and evidence of early human use of fire.
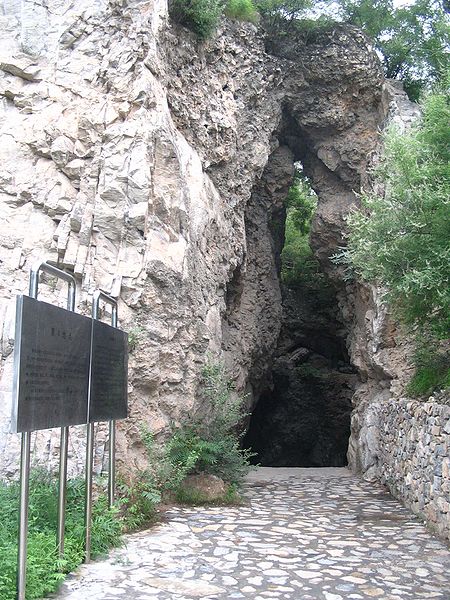
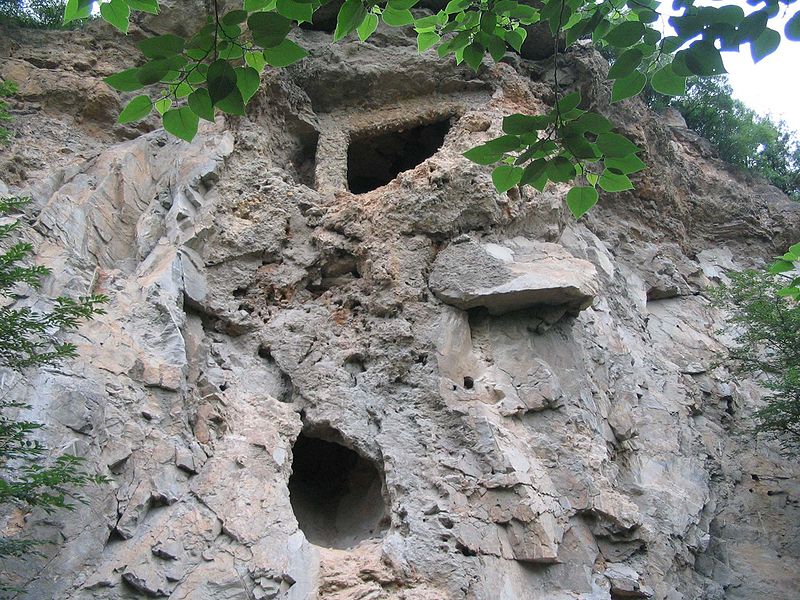
The museum at Zhoukoudian presents these discoveries through a series of exhibits and displays, meticulously detailing the significance of each find. Visitors can explore the various cave systems where the excavations took place and learn about the methods used by the scientists who worked there.
In addition to its scientific importance, Zhoukoudian offers a unique cultural perspective, highlighting the intersection of natural history and human development. The museum aims to educate the public not only about the Peking Man but also about the broader aspects of evolutionary history.
房山 (fang shan)Beijing
Zhoukoudian – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Tianyuan Cave.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to get to Zhoukoudian by public transport?
Train
- Zhoukoudian (7 min walk)
Bus
- 周口店路口 • Lines: 830, 836, 917, 房15 (31 min walk)






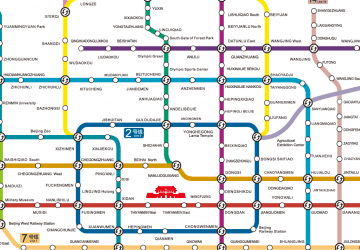 Subway
Subway