Paektu Mountain

Facts and practical information
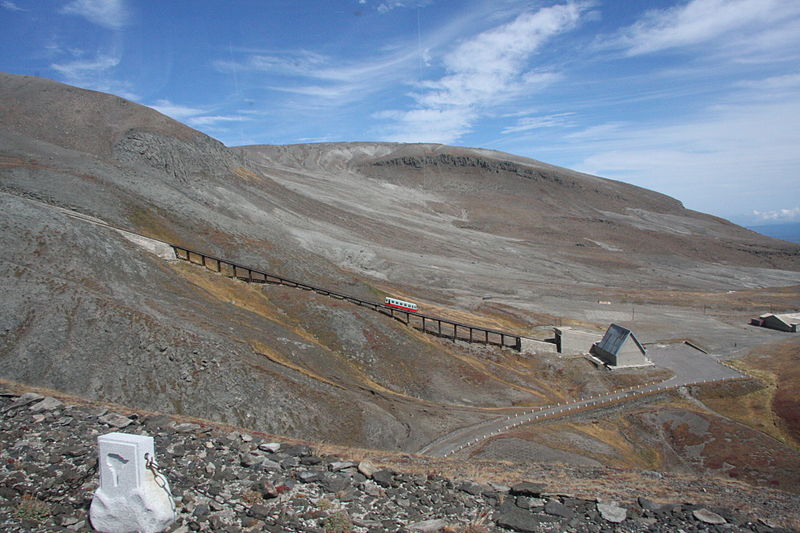
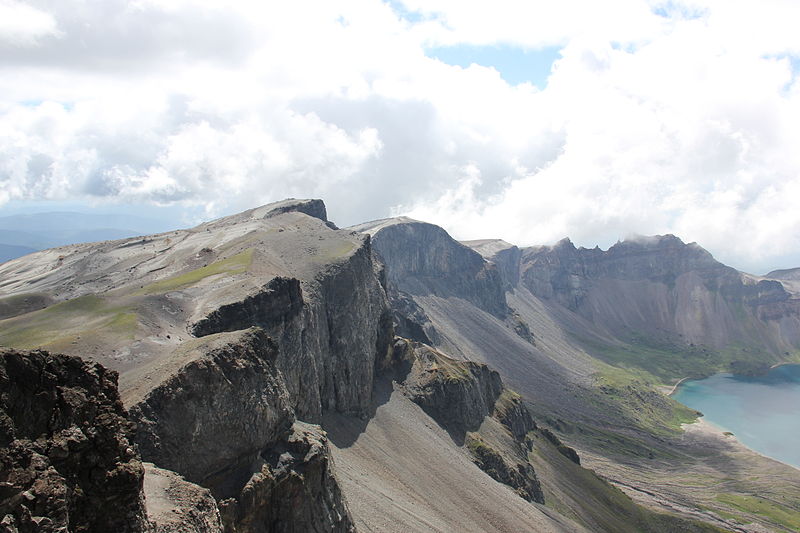
Paektu Mountain, straddling the border between China and North Korea, is a prominent natural landmark revered for its historical and cultural significance, as well as its breathtaking natural beauty. This stratovolcano, which stands at an impressive 2,744 meters, is also known as Baekdu Mountain or Changbai Mountain and is the highest peak on the Korean Peninsula.
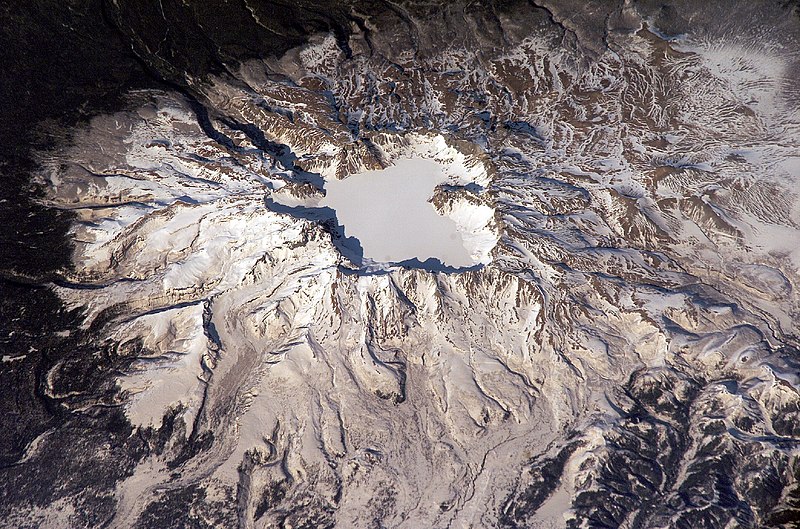
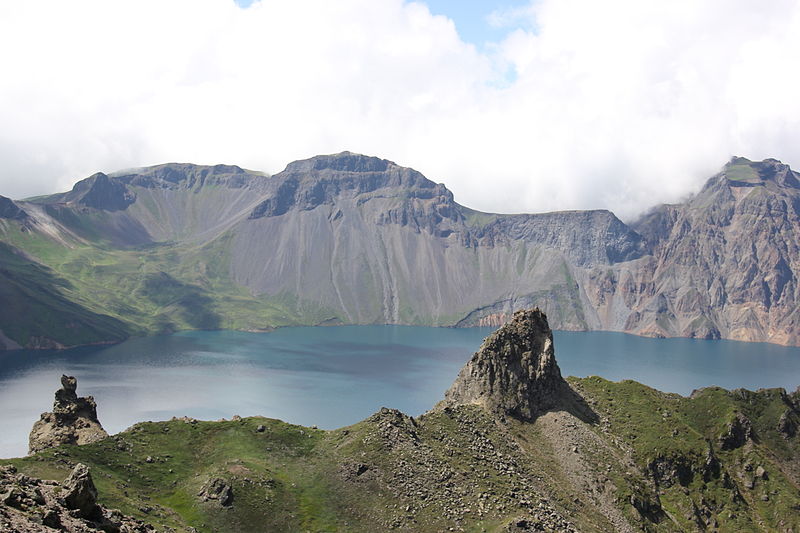
The mountain is home to the spectacular Heaven Lake, a crater lake formed by a volcanic eruption in 946 AD, which is one of the deepest lakes in the world. The area surrounding Paektu Mountain is characterized by lush forests, hot springs, and a rich biodiversity that includes many rare species, making it a valuable ecological reserve.
Historically, Paektu Mountain is considered a sacred place, especially in Korean mythology, where it is often associated with the birthplace of Dangun, the legendary founder of the first Korean kingdom. It holds a special place in Korean culture and is featured prominently in both North and South Korean iconography.
In recent times, Paektu Mountain has attracted scientists and tourists alike. The volcano is classified as dormant, with the last recorded eruption dating back to the early 20th century. Nonetheless, its volcanic status is closely monitored due to its potential impact on the region.
Jilin
Paektu Mountain – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Heaven Lake, 946 eruption of Paektu Mountain, Baekdudaegan.