Dungur, Axum

Facts and practical information
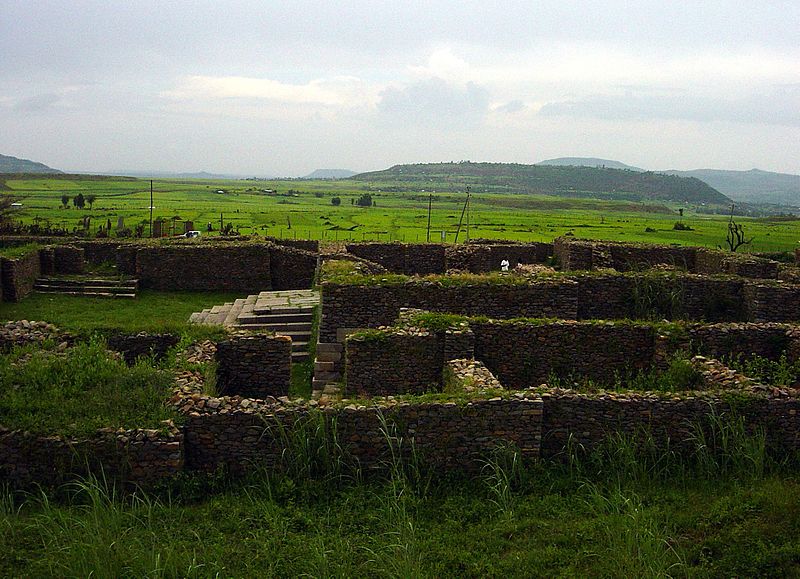
In the shadow of the ancient city of Axum, Ethiopia, lies the enigmatic archaeological site known as Dungur. Often referred to as the "Queen of Sheba's Palace," Dungur is a testament to the grandeur of the Axumite Kingdom, which once held sway over the Horn of Africa from approximately 100 AD to 940 AD.
Dungur is characterized by the remains of a large and intricate stone building, which some have romantically associated with the legendary Queen of Sheba, although no definitive evidence supports this claim. Regardless, the site offers a fascinating glimpse into the architectural prowess of a bygone era, with its finely hewn blocks of granite and thoughtfully designed layout.
The structure, dating back to somewhere between the 6th and 7th centuries, showcases the high level of civilization achieved by the Axumites. With its complex series of rooms, it reflects a sophisticated understanding of urban planning and residential design. The site includes the ruins of what are believed to be a series of stately halls, living quarters, and service areas, all arranged in a layout that suggests a purpose both ceremonial and domestic.
Despite its ruinous state, Dungur remains one of the most significant archaeological sites in Ethiopia, offering valuable insights into the cultural and historical context of the Axumite Empire. Its proximity to other important sites, such as the stelae fields and ancient tombs, makes it an essential stop for any visitor interested in the rich tapestry of Ethiopia's past.
Axum
Dungur – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion, Ezana Stone, Obelisk of Axum, King Ezana's Stele.




