Facts About Coregonus lavaretus
Coregonus lavaretus, commonly known as the lavaret or European whitefish, is a freshwater species belonging to the family Salmonidae. It is a key representative of the Coregonus genus. There is ongoing debate regarding the classification of Coregonus lavaretus and the number of species within the Coregonus genus.
Specifically, Coregonus lavaretus is found in Lake Bourget and Lake Aiguebelette within France's Rhône river basin, and it historically inhabited Lake Geneva. More broadly, the European whitefish, or common whitefish, is distributed across central and northwest Europe, extending to Siberia. This wider group is often referred to as the C. lavaretus complex, which encompasses various whitefish populations that were once considered distinct species. Genetic studies suggest that most of the diversity within this complex developed after the last ice age.
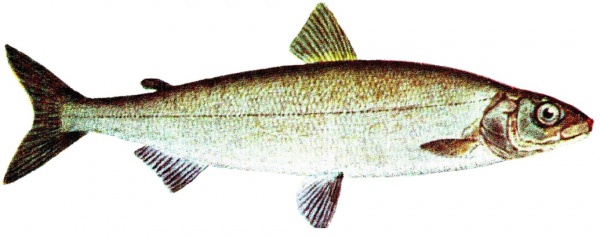
European whitefish exhibit a variety of forms but generally possess a streamlined body, a slightly protruding upper jaw, and a fleshy dorsal fin—traits characteristic of salmonids. Their diet predominantly consists of benthic invertebrates and zooplankton, though larger individuals also consume insects and small fish. They spawn in the autumn, with timing contingent on water temperature. Some populations migrate upstream to rivers for spawning, while others remain in lakes or coastal areas. European whitefish typically reach about 55 cm in length and weigh approximately 2 kg.
 Norway
Norway