Facts About Brown-cheeked hornbill
The brown-cheeked hornbill is a striking bird found in West African countries such as Ivory Coast, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Sierra Leone, and Togo. It thrives in tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, plantations, and secondary growth forests. However, this magnificent bird faces significant threats from habitat destruction due to logging and forest fragmentation.
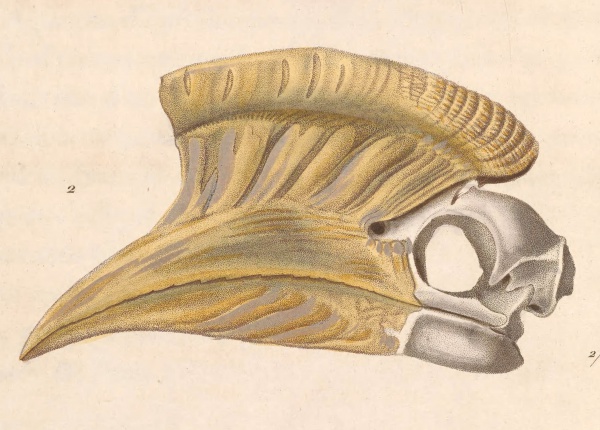
Visually, the brown-cheeked hornbill is a large bird with several distinctive features. It has a yellow down-curved beak, reddish-brown cheeks, and a white rump, belly, and tail. Males and females can be differentiated by the color of their beaks and casques: males possess yellow ones, while females have black.
Native to the Upper Guinean forests in tropical West Africa, this hornbill covers vast distances in search of fruits and insects, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal and forest regeneration. Its habitat primarily comprises moist deciduous and semi-evergreen mixed forests.
Unfortunately, the brown-cheeked hornbill is vulnerable due to forest fragmentation and timber extraction, which diminish its habitat and food sources. Moreover, it is at risk from hunting for the live bird trade and bushmeat. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has classified this bird as "vulnerable" underscoring the urgent need for conservation efforts to protect it.
 Cameroon
Cameroon