
The Gambia Travel Safety
Travel Safety in The Gambia
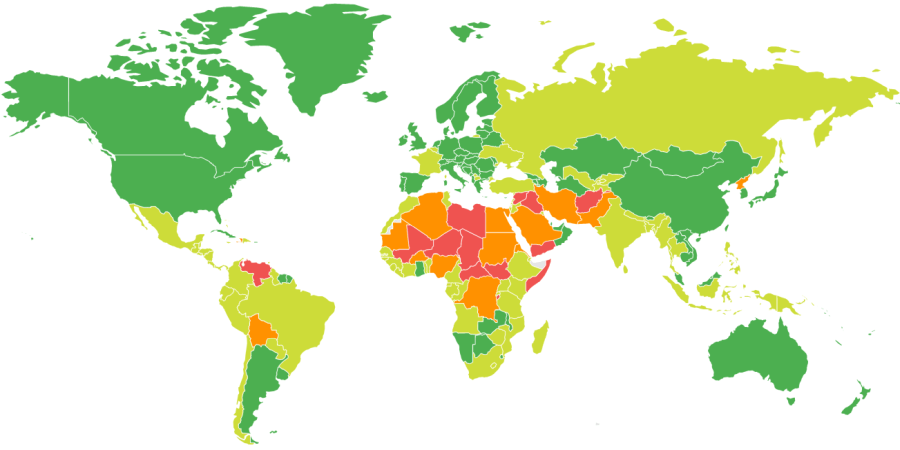
General travel safety in The Gambia on a scale of 1 to 4 — where 1 is safe and 4 is dangerous. Data compiled on the basis of Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs.
Country
The Gambia
Updates
Updated: 26 Jun 2025 • Still current at: 2 Jul 2025
Status
LEVEL 2 - Exercise a high degree of caution
There are more or higher risks than what you would typically find at locations with level 1. You should do your research and take extra precautions. The level may reflect a weak law-and-order system, where violent crime is common. The destination may lack some key public services, such as a responsive police force. In some cases, there may be a risk that the security environment could change with little warning. This level may also reflect a passing event, such as political unrest or a short-term increase in a location's domestic terrorism level.
Safety and Security Tips
General safety
Do not show signs of affluence and ensure that personal belongings and travel documents are secure at all times. You should keep informed of local developments that could affect your safety. Tourist facilities are limited outside of Banjul.
Precautions
Ensure that your travel documents and valuable items are secure. Theft from vehicles has increased. Car doors should be locked and car windows closed at all times. Beware of men (so-called "bumsters") who offer to be tour guides, as they are likely to demand payment afterwards, even if that was not previously agreed upon. Politely decline any unsolicited offer. Check with local authorities to determine which beaches are safe. Do not bring valuables or large sums of money to the beach. Avoid isolated beaches.
Road safety
Most roads outside the capital are unpaved. Overland travel can be difficult without a four-wheel-drive vehicle, particularly during the rainy season. In the greater Banjul area, main roads are paved but are narrow, potholed and poorly lit. Avoid driving outside urban areas after dark. Contact the nearest police station if involved in a traffic accident. Police roadblocks are common throughout the country and identification documents may be requested. Stop at all security roadblocks and checkpoints and cooperate with local authorities.
Regional travel
Travellers have been attacked on roads leading north from Ziguinchor (Senegal) to Banjul (Gambia) and on Senegalese roads from Bignona to Senoba, which is near the Senegal's Gambia border. Be careful when travelling overland to the Casamance region in Senegal, as separatist rebels operate in this area. You should also consult the Travel Advice and Advisories for Senegal before departing. It is dangerous to cross the Gambia River on wooden pirogues,due to overcrowding and the lack of security measures.
Women's safety
In Gambia beware of "bumsters" - local men who approach tourists, particularly on beaches and tourist zones, offering help, to act as local guides or to enter into a relationship. Women should be vigilant all the time and aware of the surroundings. Avoid dark or non-tourist areas at night. Instead try to be around larger crowds, whether they are fellow tourists or local citizens. Females should be cautious while dealing with strangers and acquaintances. Women may be subject to unpleasant male attention, sexual harassment and verbal abuse. Avoid flash of money or valuables in public. Exercise a high degree of caution during travel.
Fraud
Cases of attempted fraud occur.
Crime
Petty crime such as pickpocketing and purse snatching is common, particularly in crowded markets and on ferries. Theft from hotel rooms is also common.
Update 1 November 2020Emergency Calls
- Police117 or 112
- Fire118
- Ambulance116
Embassy of de
German Embassy Office in Banjul
AddressOffice of the German Ambassador
Local Law and Culture
Culture
The majority of the population is Muslim. Gambia's customs, laws and regulations adhere closely to Islamic practices and beliefs. Exercise common sense and discretion in dress and behaviour. Dress conservatively: for women, knee-length or longer dresses and long sleeves are preferable, women should avoid clothing that could be construed as revealing, such as miniskirts, shorts and sleeveless or low-cut (front or back) blouses and tops., and men should not wear shorts outside tourist areas. Respect religious and social traditions to avoid offending local sensitivities. Overt public displays of intimate affection are frowned upon in Gambia culture. During the lunar month of Ramadan, use discretion when drinking, eating, and smoking in public between sunrise and sunset.
LGBT
The laws of the Gambia prohibit sexual acts between individuals of the same sex. Those convicted can face penalty upto life imprisonment. LGBT travellers should carefully consider the risks of travelling to the Gambia.
Illegal or restricted activities
The use of drugs is prohibited. Convicted offenders could be punished by detention or other penalties. Penalties for importing or exporting drugs or contraband are strict. Never accept packages from strangers and pack your luggage yourself. Libel, sedition and slander are criminal offences. Convicted offenders can expect prison terms without any option of a fine. Some medications and skin-bleaching creams are subject to strict import and export laws. Visitors could face fines and/or imprisonment if they arrive in the Gambia with substances containing betamethasone, clobetatol, clobetatone, fluocinonide, hydrocortisone or hydroquinone. Photography of airports, government buildings, military installations and embassies is prohibited.
Driving
An International Driving Permit is recommended.
Update 1 November 2020Vaccinations and Medications
A doctor's consultation is required prior to any vaccinations being administered. This section is for informational purposes and does not exhaust all issues related to vaccination. Please contact your doctor for complete information on this subject.
Stay Healthy and Safe
Act in advance of to prevent. Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least 4-8 weeks before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need.
All travelers
You should be up to date on routine vaccinations while traveling to any destination. Some vaccinations may also be required in The Gambia.
Before each trip, it is worth making sure that we are up to date with the routine vaccinations. These include vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, chickenpox, polio and flu.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Most travelers
Get travel vaccines and medicines because there is a risk of these diseases in the country you are visiting.
Hepatitis A is a digestive disease caused by the hepatitis A virus and is closely related to a lack of good hygiene.
It can be asymptomatic, moderate, or very severe.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Take antimalarial meds
- Prevent bug bites
Estimated relative risk of malaria in The Gambia
Wysokie
Areas with malaria
All
Typhoid fever is an acute, systemic infectious disease caused by Salmonella typhi.
The source of the infection may include dirty water, raw fruits, vegetables, dairy products, as well as dirt containing bacteria.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Yellow fever is an acute viral disease which is transmitted by virus-infected mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Prevent bug bites
Vaccination requirements
Required if traveling from a country with risk of YFV transmission and ≥9 months of age.
Some travelers
Vaccinations and medications that may be recommended under certain conditions, depending on where you will be, the length of your stay and the nature of your stay.
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Infection occurs through contact of injured skin or mucous membranes with virus-infected blood or other secretions (e.g. during sexual contact, through contaminated needles or as a result of medical procedures).
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Avoid sharing body fluids
- Avoid non-sterile medical or cosmetic equipment
Meningococcal disease is any illness caused by a type of bacteria called Neisseria meningitidis.
Infection occurs through droplets - through contact with the secretion of the patient or the host, e.g. when coughing, sneezing, kissing or sharing cutlery or dishes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by neurotrophic viruses from the rhabdovirus family.
The infection is most often caused by biting a sick animal or other contact of its saliva with mucous membranes, conjunctiva or damaged skin.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Keep away from animals
We have made every effort to ensure that the information presented reliably reflects the general safety situation in a given place. However, the data is provided for informational purposes only and we do not take responsibility for any damages or losses resulting from incorrect risk assessment. Before each trip, we recommend checking the current situation in the country of destination on the websites of the relevant Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 Senegal
Senegal