Soputan


Facts and practical information
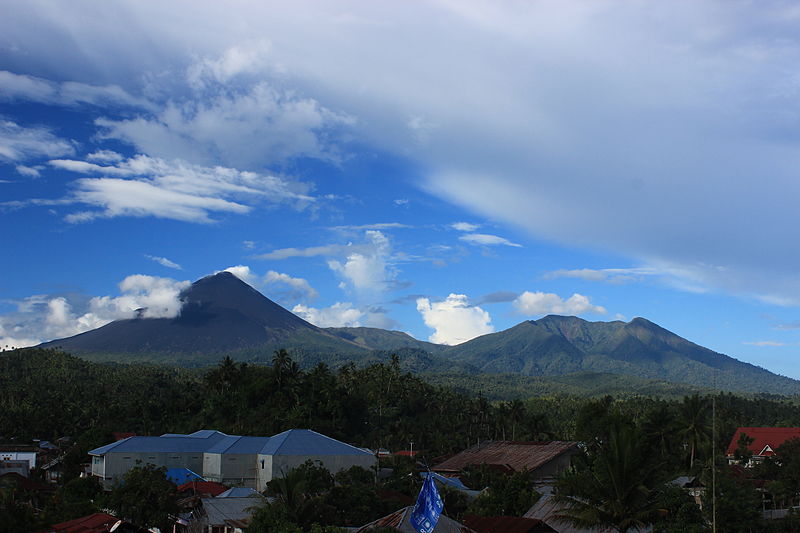
Soputan, located on the northern arm of the island of Sulawesi in Indonesia, is one of the nation's most active volcanoes. With its first recorded eruption in 1785, Soputan has since experienced a series of eruptions that have shaped the surrounding landscape and impacted local communities.
Dominating the Minahasa Peninsula's skyline, the stratovolcano boasts a conical shape with a summit elevation of 1,784 meters. Soputan's frequent activity is characterized by explosive eruptions and pyroclastic flows, which are hot avalanches of volcanic ash, gas, and rocks that race down the slopes at high speeds. These eruptions pose significant risks to the nearby populations and agriculture, prompting authorities to maintain strict monitoring and issue timely warnings when activity intensifies.
Soputan's most recent eruptions have underscored the volcano's unpredictability and the importance of disaster preparedness in the region. Despite the dangers, the area surrounding Soputan is rich in biodiversity, and the fertile volcanic soils support a variety of crops, contributing to the local economy.
Research and studies continue to focus on understanding Soputan's behavior to improve eruption forecasting. The Indonesian Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation (CVGHM) closely observes the volcano, providing vital information to ensure the safety and preparedness of the residents.
North Sulawesi
Soputan – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Mount Sempu.