Sinabung

Facts and practical information
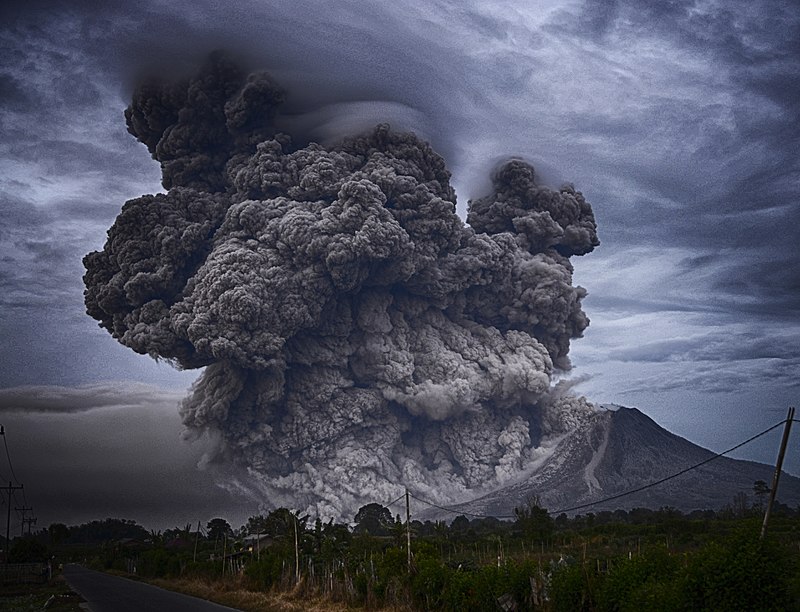
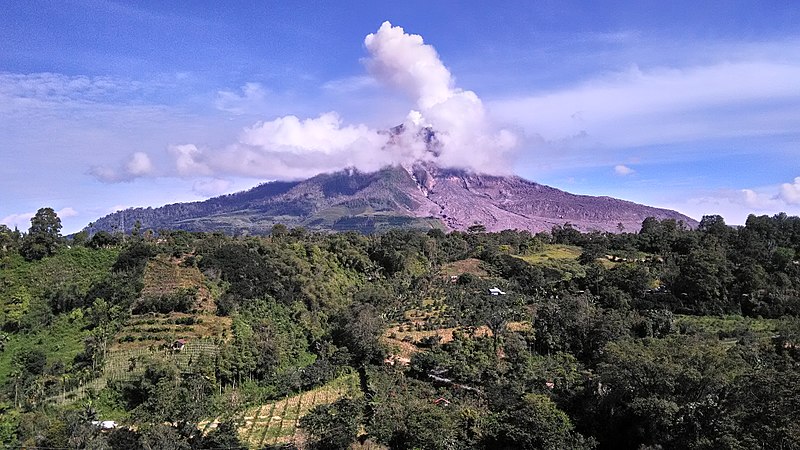
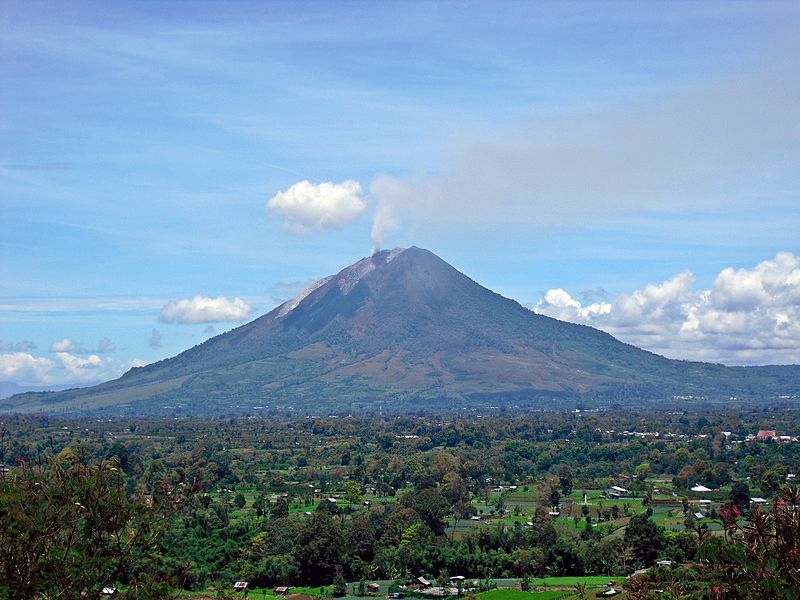
Mount Sinabung, located in North Sumatra, Indonesia, is one of the most active volcanoes in the region. This stratovolcano, standing at a formidable height of 2,460 meters, has become infamous for its eruptions in the 21st century, particularly after lying dormant for nearly 400 years.
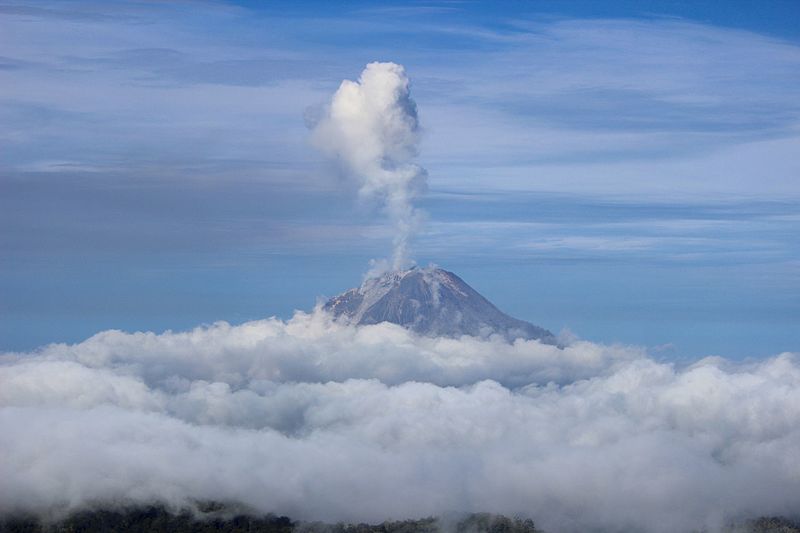
The volcano reawakened in 2010, and since then, it has erupted multiple times, causing significant disruptions to the local communities, including displacement of residents and damage to agriculture. The most devastating eruptions occurred in 2014 and 2016, leading to fatalities and the declaration of exclusion zones due to the dangers posed by pyroclastic flows, lava, and ash.
Despite the risks, Mount Sinabung has garnered attention from both scientists and tourists. Researchers are drawn to the volcano for its insights into volcanic behavior and the mechanisms of eruptions. Meanwhile, tourists are attracted to the dramatic landscapes and the opportunity to witness the raw power of nature from a safe distance.
The Indonesian government, along with various geological agencies, closely monitors the activity of Mount Sinabung. Warning systems and evacuation plans are in place to protect the lives of those in the proximity of the volcano. The ongoing geological activity serves as a reminder of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of our planet's surface.
Sejarah gunung sinabungNorth Sumatra