Uruk

Facts and practical information
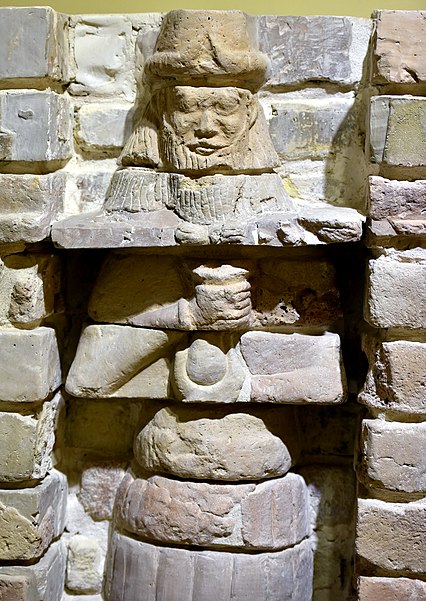
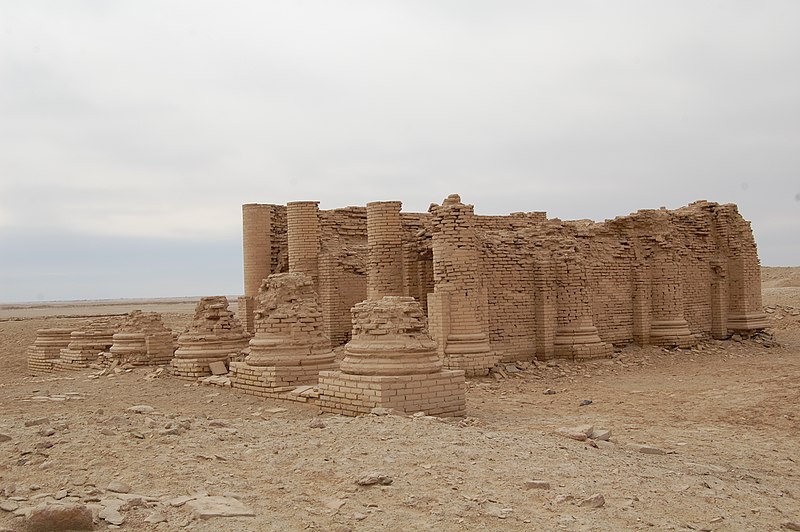
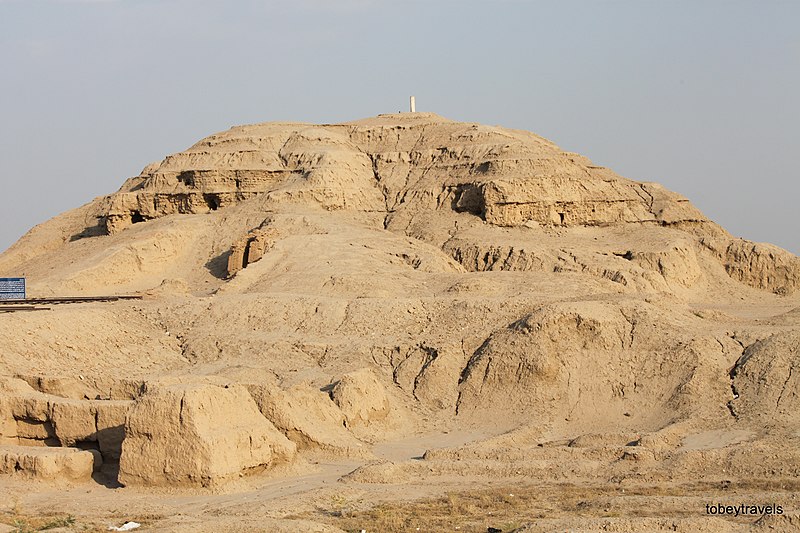
Uruk, Iraq, an archaeological site of immense historical significance, is considered one of the cradles of civilization. Located in the southern region of Mesopotamia, it was one of the most important cities in ancient Sumer and is thought to have been the largest city in the world during its zenith around 2800 BCE. Uruk played a fundamental role in the urbanization and cultural progress of humanity.
The site is famed for its impressive architectural remains, including the massive ziggurat and the city's walls, believed to have been constructed under the direction of the legendary King Gilgamesh. This king, who later became the central figure in the Epic of Gilgamesh, is thought to have presided over a period of considerable construction and urban development.
Uruk is also recognized for its contributions to writing; it is where some of the earliest examples of cuneiform script were discovered, marking a pivotal advancement in the history of writing. These clay tablets provide valuable insights into the economic, social, and political aspects of early urban life.
Excavations at Uruk have unearthed a wealth of artifacts, including intricate cylinder seals, monumental religious buildings, and elaborate artworks, reflecting the city's status as a hub of ancient craftsmanship and religious practice.
Al-Muthannia