Qumran

Facts and practical information
Nestled in the Judaean Desert of Israel, the ancient site of Qumran holds a historical and religious significance that resonates far beyond its remote location. Famed as the discovery site of the Dead Sea Scrolls, Qumran is an archaeological treasure that offers invaluable insight into the Jewish culture of the Second Temple period.
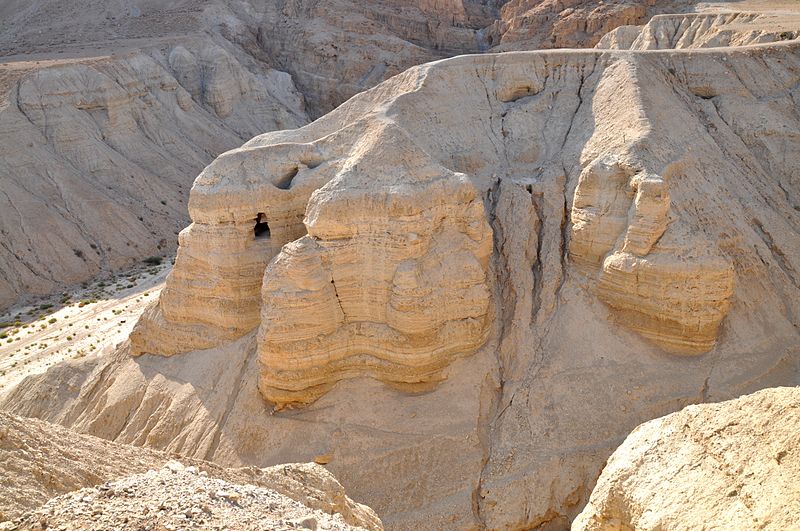
Uncovered in 1947, the Dead Sea Scrolls are a collection of Jewish texts that were hidden in the caves of Qumran around the time of the destruction of the Second Temple in 70 CE. The scrolls comprise a wide array of writings, including biblical manuscripts, apocryphal works, and sectarian documents, which are believed to have been penned by the Essenes, a Jewish sect that lived in Qumran during the Hellenistic and Roman periods.
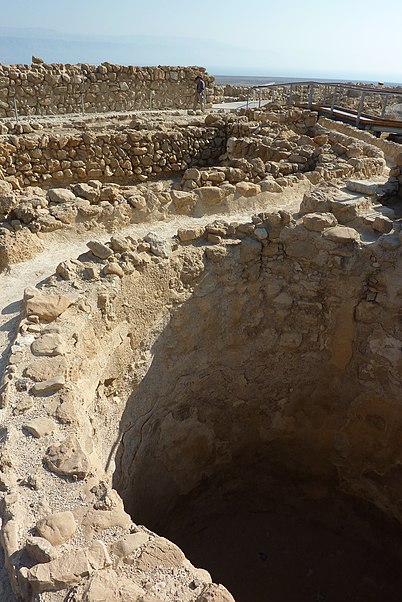
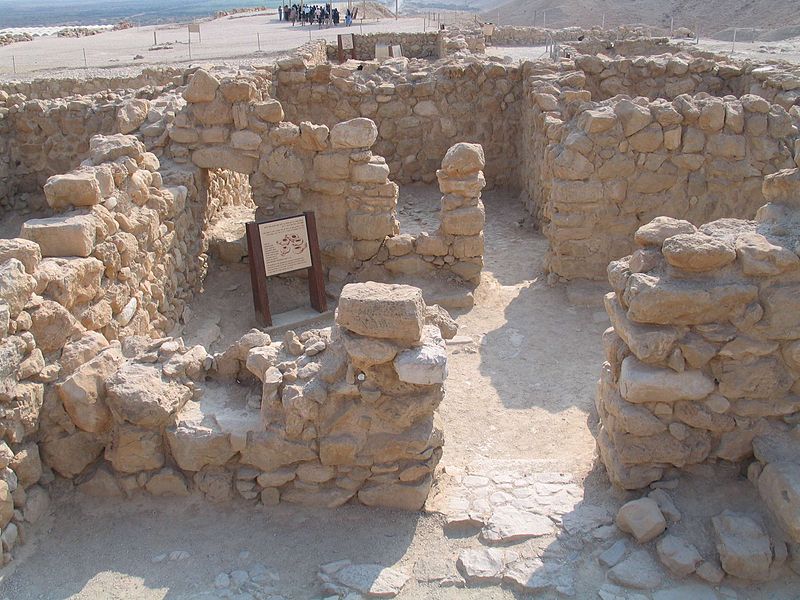
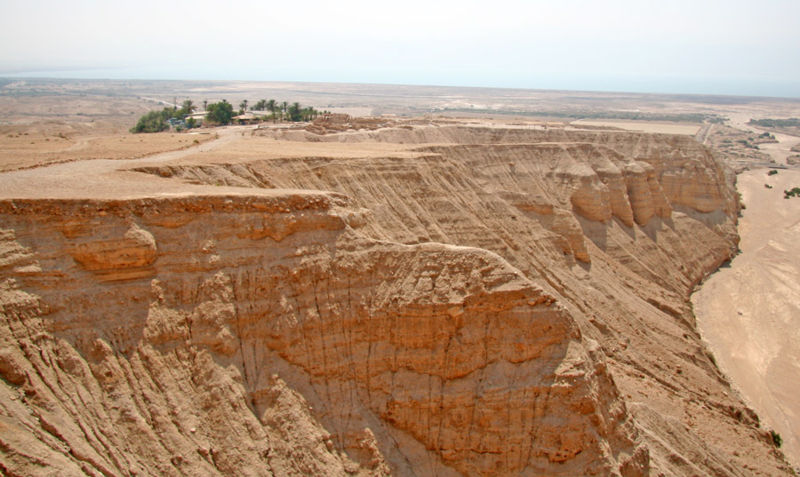
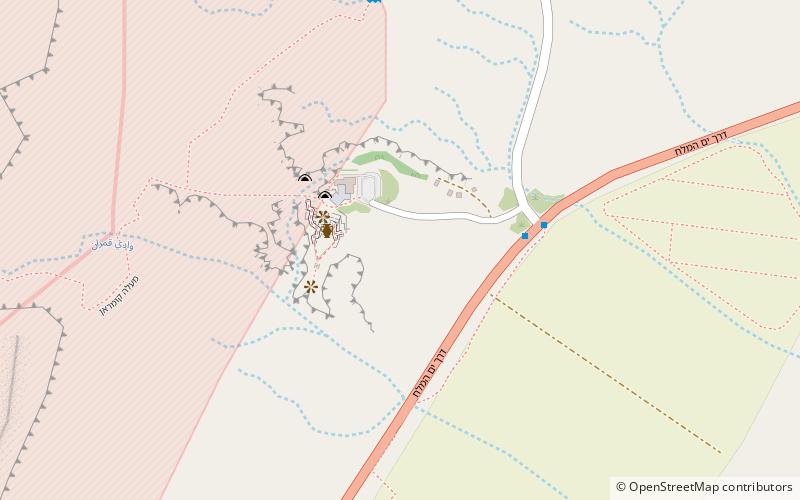
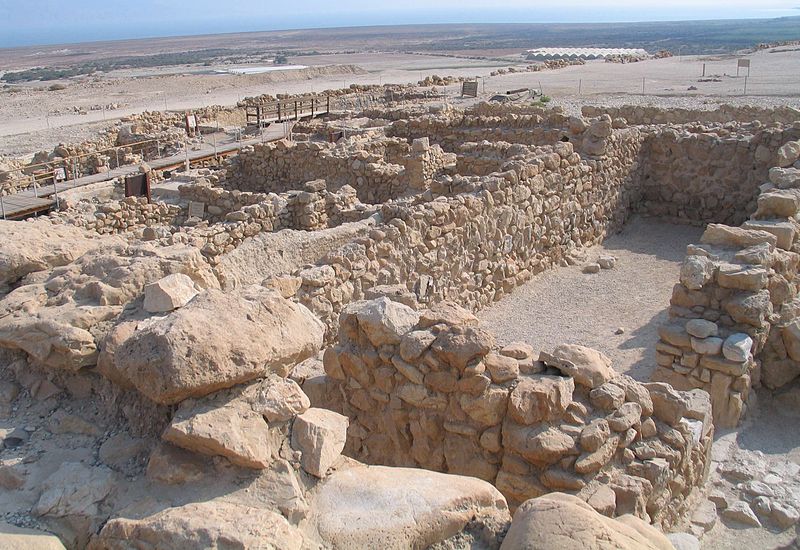
The ruins of Qumran are situated on a plateau above the northwestern shore of the Dead Sea. Excavations of the site have revealed a complex of buildings comprising residential quarters, communal rooms, a central dining room, and ritual baths, all of which paint a picture of a highly organized and ascetic community life. Among the most intriguing findings are the numerous inkwells discovered, suggesting that this was a center of intense scribal activity.
Qumran – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Deir Hajla, Einot Tzukim, Qumran cemetery, Hyrcania Fortress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
When is Qumran open?
- Monday 8 am - 5 pm
- Tuesday 8 am - 5 pm
- Wednesday 8 am - 5 pm
- Thursday 8 am - 5 pm
- Friday 8 am - 4 pm
- Saturday 8 am - 4 pm
- Sunday 8 am - 5 pm