Sierra Negra

Facts and practical information
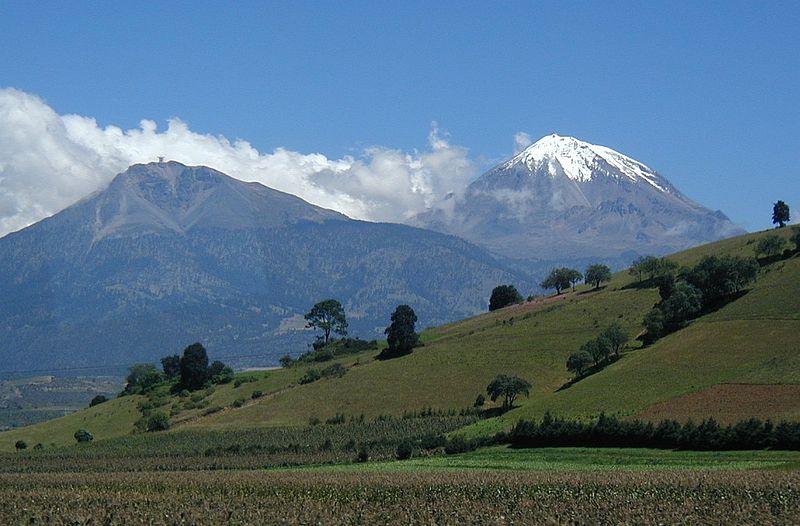
Sierra Negra, an imposing volcano located in the southern Mexican state of Puebla, is one of the most significant geological features in the region. Known as the birthplace of the largest lava flow in the 20th century, Sierra Negra boasts a massive caldera measuring approximately 1.5 kilometers in diameter. This majestic volcano, which stands at an elevation of around 4,580 meters above sea level, is the fifth-highest peak in Mexico.
Sierra Negra, also known as Black Mountain due to the dark lava rock that composes much of its surface, is a companion to the larger and more famous Pico de Orizaba, Mexico's highest mountain and North America's third-highest peak. Together, they form part of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt and are a draw for geologists, volcanologists, and adventure enthusiasts alike.
The last major eruption of Sierra Negra occurred in 2005, a powerful reminder of the ever-present forces of nature that shape our planet. The volcano is closely monitored by scientists for seismic activity and other signs of potential eruptions. Its slopes are also home to a variety of ecosystems, ranging from pine-oak forests to high-altitude grasslands, supporting diverse wildlife.
For those seeking to explore the Sierra Negra, it offers a challenging yet rewarding hiking experience. The journey to the summit provides breathtaking views and a rare opportunity to stand atop an active volcano. However, due to its high altitude and active status, visitors must take caution and often require a guide for safe passage.
In the world of science, Sierra Negra is home to the Large Millimeter Telescope (LMT), the world's largest single-dish steerable millimeter-wavelength telescope designed for astronomical observations. This impressive facility underscores the importance of Sierra Negra not only as a natural wonder but also as a site of significant scientific inquiry.
Puebla
Sierra Negra – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Pico de Orizaba, Large Millimeter Telescope, Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, High Altitude Water Cherenkov Experiment.




