Pico de Orizaba

Facts and practical information
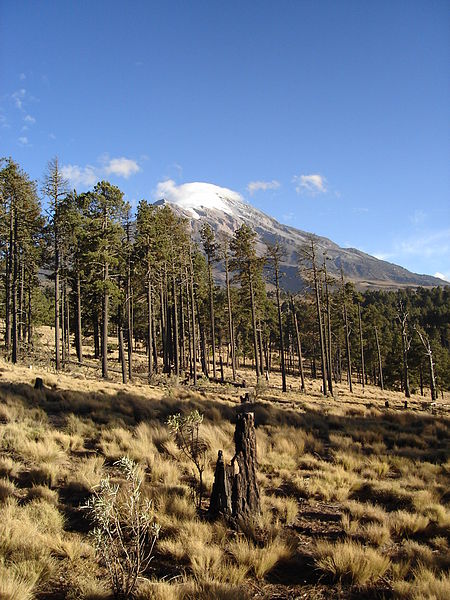
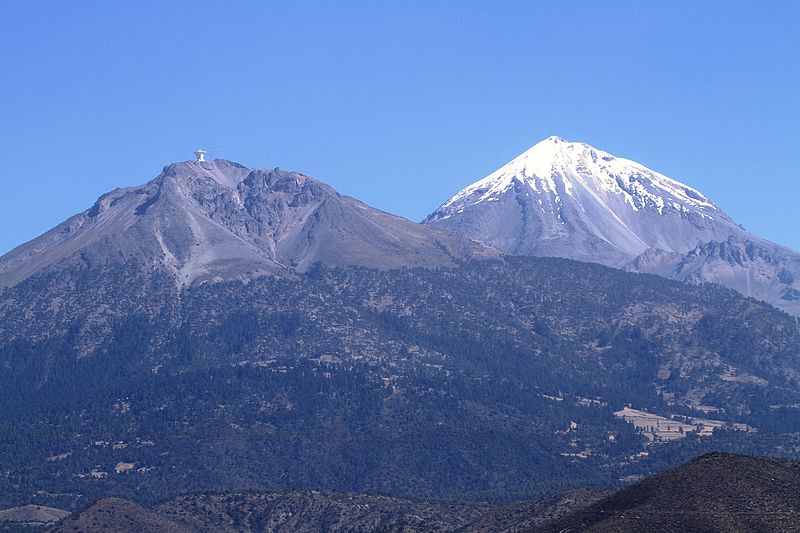
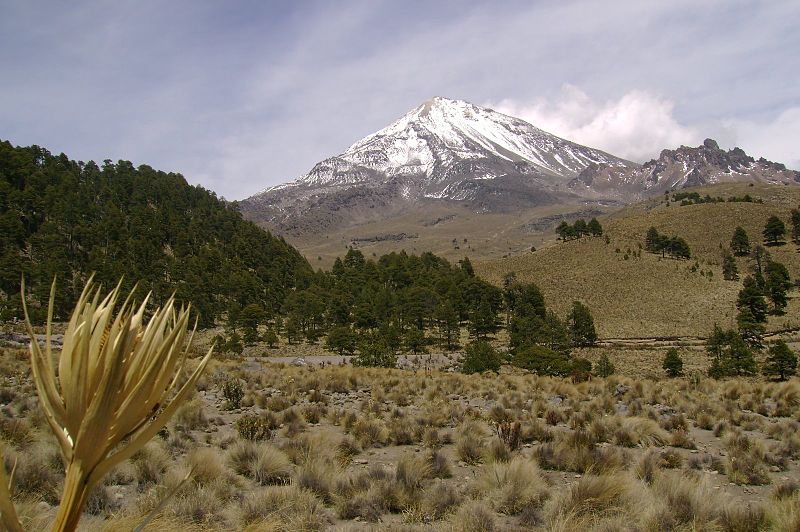
Pico de Orizaba, also known as Citlaltépetl, stands majestically as Mexico's highest peak and North America's third highest mountain. This dormant stratovolcano, reaching an imposing height of 5,636 meters, is not only a geographical landmark but also a beacon for mountaineers and adventure seekers from around the world. Situated at the border between the states of Puebla and Veracruz, Pico de Orizaba is part of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt and is recognized as a significant natural wonder in Mexico.
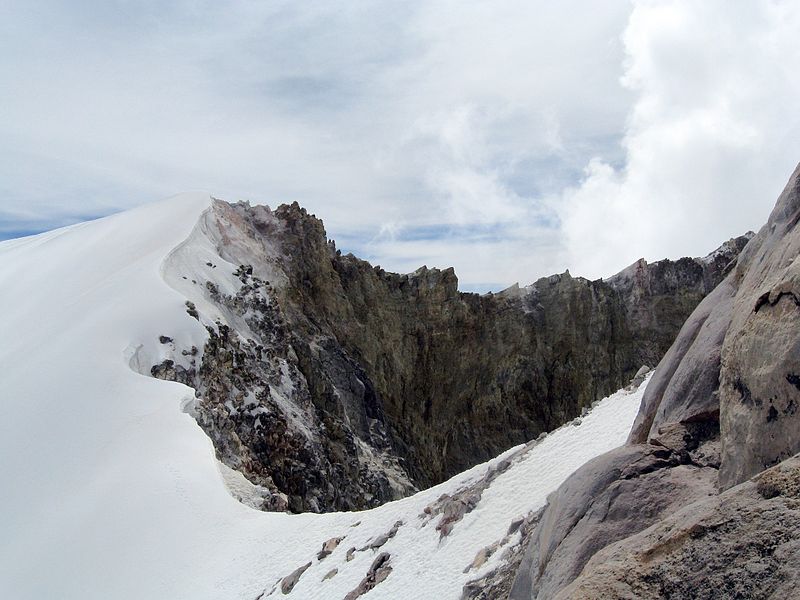
The volcano has a glacial crown, which is the source of a number of rivers, thus playing a crucial role in the region's hydrology. The Pico de Orizaba National Park, which surrounds the volcano, is a haven for biodiversity, hosting various species of plants and wildlife, some of which are endemic to the area.
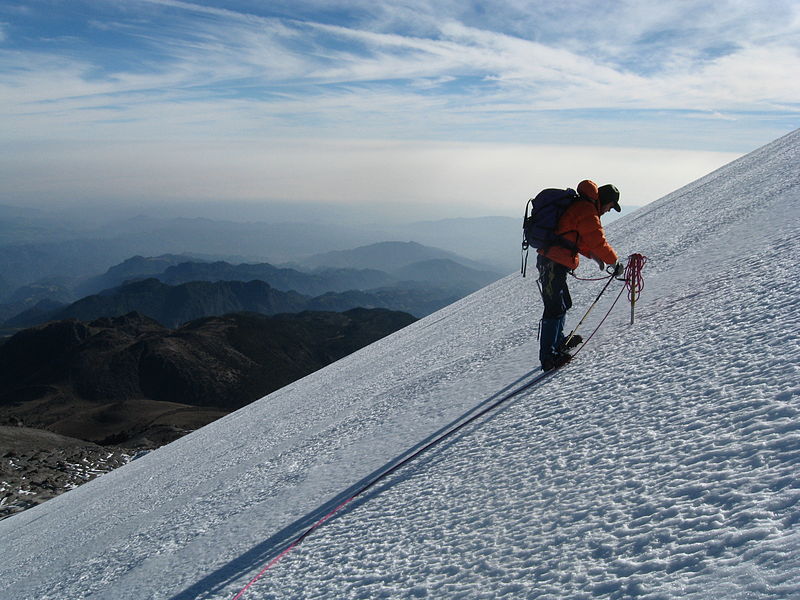
Climbing Pico de Orizaba is a challenging endeavor due to its high altitude and the presence of glaciers. However, it attracts numerous climbers every year who aim to reach the summit and experience the breathtaking views across Mexico's landscape. The ascent typically starts from the town of Tlachichuca, with the climbing season running from October to March when the weather conditions are most favorable.
The history of Pico de Orizaba is steeped in the cultural heritage of the region, with its name deriving from the Nahuatl language, meaning "Star Mountain." It is also a site of historical significance, as it served as a reference point for early explorers and has featured prominently in local legends and folklore.
Puebla
Pico de Orizaba – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Sierra Negra, Large Millimeter Telescope, Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt, High Altitude Water Cherenkov Experiment.