
Nepal Travel Safety
Travel Safety in Nepal
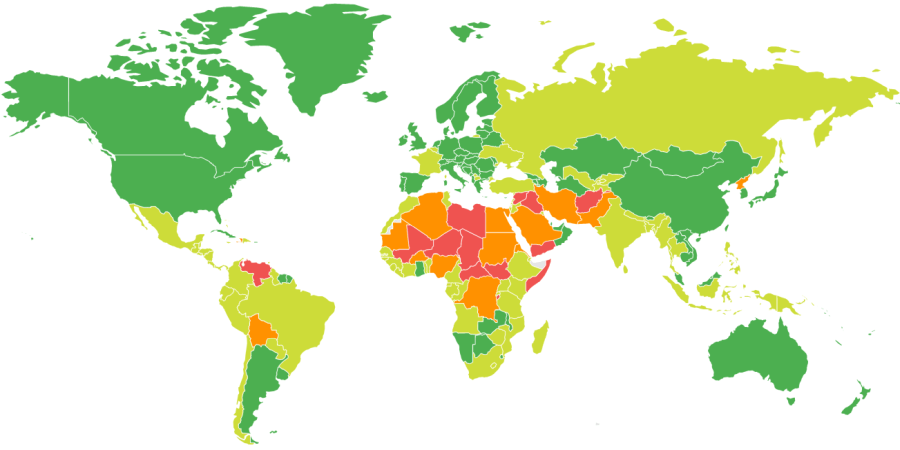
General travel safety in Nepal on a scale of 1 to 4 — where 1 is safe and 4 is dangerous. Data compiled on the basis of Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs.
Country
Nepal
Updates
Updated: 26 Jun 2025 • Still current at: 2 Jul 2025
Status
LEVEL 2 - Exercise a high degree of caution
There are more or higher risks than what you would typically find at locations with level 1. You should do your research and take extra precautions. The level may reflect a weak law-and-order system, where violent crime is common. The destination may lack some key public services, such as a responsive police force. In some cases, there may be a risk that the security environment could change with little warning. This level may also reflect a passing event, such as political unrest or a short-term increase in a location's domestic terrorism level.
Safety and Security Tips
Road safety
Exercise caution when travelling by road as road conditions and driving standards are poor and traffic laws are not enforced. Drivers often drive at excessive speed and often do not yield right-of-way to pedestrians.
Women's safety
Women are vulnerable to harassment and verbal abuse. Sexual assaults against foreign nationals, particularly women, have been reported in tourist areas, including Thamel and Sanepa in Kathmandu. Be wary of accepting drinks from strangers, don't leave drinks unattended and exercise caution, especially when alone after dark.
Crime
Petty theft is common, particularly near tourist sites, on buses and in hotel rooms. Take particular care when walking around Kupandol, Sanepa and Thamel, popular tourist spots in Kathmandu, where pickpocketing is common.
Update 1 November 2020Emergency Calls
- Police100 or 112
- Fire101 or 112
- Ambulance102 or 112
Embassy of fr
French Embassy in Kathmandu
AddressLazimpat
(+977) 1 4 414734
(+977) 1 4 418288
Local Law and Culture
Culture
Women should dress conservatively in public. Public displays of affection are considered to be inappropriate at many of Nepal's religious sites.
Illegal drugs
Penalties for possession, use or trafficking of illegal drugs are severe. Convicted offenders can expect jail sentences, including life imprisonment, and heavy fines. Possession of small amounts of marijuana can lead to a prison sentence of over 5 years, usually after a lengthy and expensive legal process.
Wild animals
It's illegal to buy, sell, kill or capture any wild animal or trade its parts without a license.
Driving
Traffic drives on the left. You must carry an International Driving Permit. There is zero tolerance for driving under the influence of alcohol. Helmets are mandatory for motorcycle drivers.
Update 1 November 2020Vaccinations and Medications
A doctor's consultation is required prior to any vaccinations being administered. This section is for informational purposes and does not exhaust all issues related to vaccination. Please contact your doctor for complete information on this subject.
Stay Healthy and Safe
Act in advance of to prevent. Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least 4-8 weeks before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need.
All travelers
You should be up to date on routine vaccinations while traveling to any destination. Some vaccinations may also be required in Nepal.
Before each trip, it is worth making sure that we are up to date with the routine vaccinations. These include vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, chickenpox, polio and flu.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Most travelers
Get travel vaccines and medicines because there is a risk of these diseases in the country you are visiting.
Hepatitis A is a digestive disease caused by the hepatitis A virus and is closely related to a lack of good hygiene.
It can be asymptomatic, moderate, or very severe.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Typhoid fever is an acute, systemic infectious disease caused by Salmonella typhi.
The source of the infection may include dirty water, raw fruits, vegetables, dairy products, as well as dirt containing bacteria.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Some travelers
Vaccinations and medications that may be recommended under certain conditions, depending on where you will be, the length of your stay and the nature of your stay.
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Infection occurs through contact of injured skin or mucous membranes with virus-infected blood or other secretions (e.g. during sexual contact, through contaminated needles or as a result of medical procedures).
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Avoid sharing body fluids
- Avoid non-sterile medical or cosmetic equipment
Japanese encephalitis is an infectious disease caused by arboviruses from the same family of microbes (Flaviviridae) that cause yellow fever or tick-borne encephalitis.
The vector of infection is mosquitoes of the genus Culex and Aedes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Prevent bug bites
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Take antimalarial meds
- Prevent bug bites
Estimated relative risk of malaria in Nepal
Niskie
Areas with malaria
Present throughout the country at altitudes <2000 m (6562 ft). None in Kathmandu and on typical Himalayan treks
Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by neurotrophic viruses from the rhabdovirus family.
The infection is most often caused by biting a sick animal or other contact of its saliva with mucous membranes, conjunctiva or damaged skin.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Keep away from animals
Yellow fever is an acute viral disease which is transmitted by virus-infected mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Prevent bug bites
Vaccination requirements
Required if traveling from a country with risk of YFV transmission and ≥1 year of age, including transit >12 hours in an airport located in a country with risk of YFV transmission.
We have made every effort to ensure that the information presented reliably reflects the general safety situation in a given place. However, the data is provided for informational purposes only and we do not take responsibility for any damages or losses resulting from incorrect risk assessment. Before each trip, we recommend checking the current situation in the country of destination on the websites of the relevant Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 India
India