Dabotap, Gyeongju

Facts and practical information
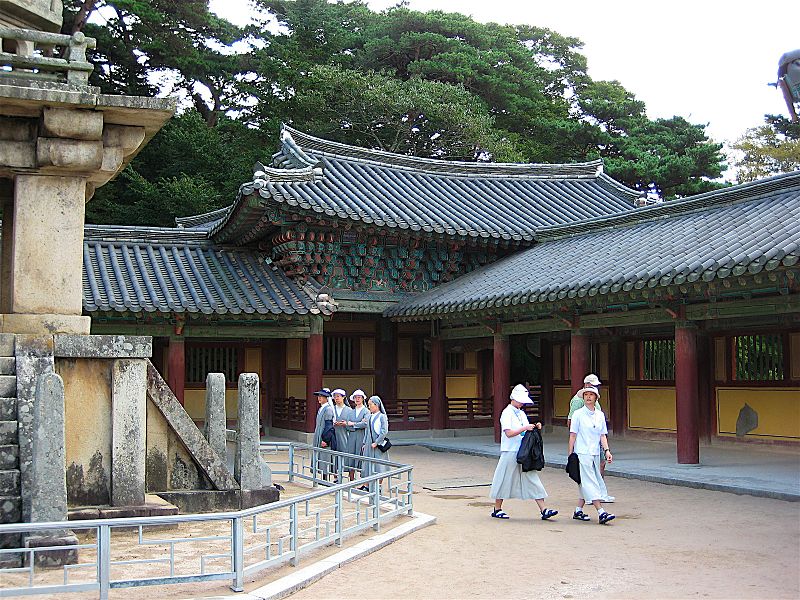
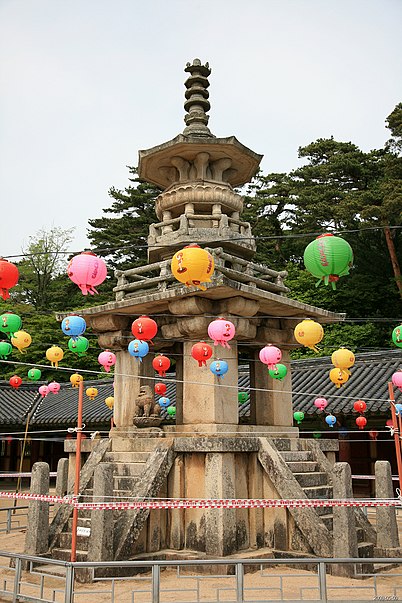
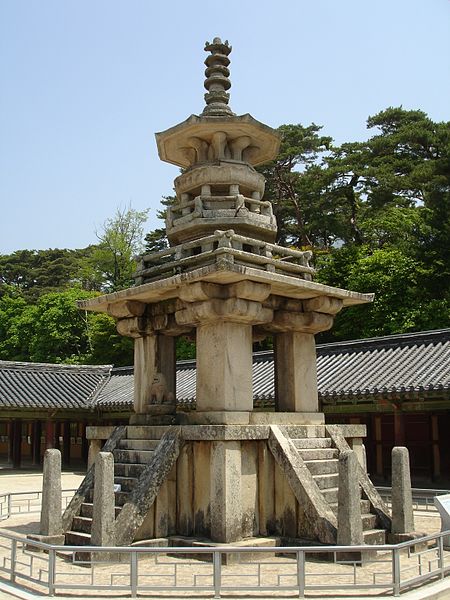
Dabotap, also known as the Pagoda of Many Treasures, is an iconic structure located in the heart of the historical city of Gyeongju, South Korea. This distinctive pagoda, believed to have been constructed in 774 during the Unified Silla period, is part of the temple complex of Bulguksa, which has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage site. Standing approximately 10.4 meters tall, Dabotap is celebrated for its intricate design and the harmonious blend of symmetry and asymmetry that is unique among East Asian pagodas.
The pagoda is composed of multiple stone tiers, each elaborately carved with figures and designs that reflect Buddhist iconography. Unlike the conventional straight-lined pagodas, Dabotap showcases an elaborate form with octagonal and square shapes, which give it a sense of movement and complexity. The pagoda is also adorned with stone staircases and balustrades that are masterpieces of stone craftsmanship.
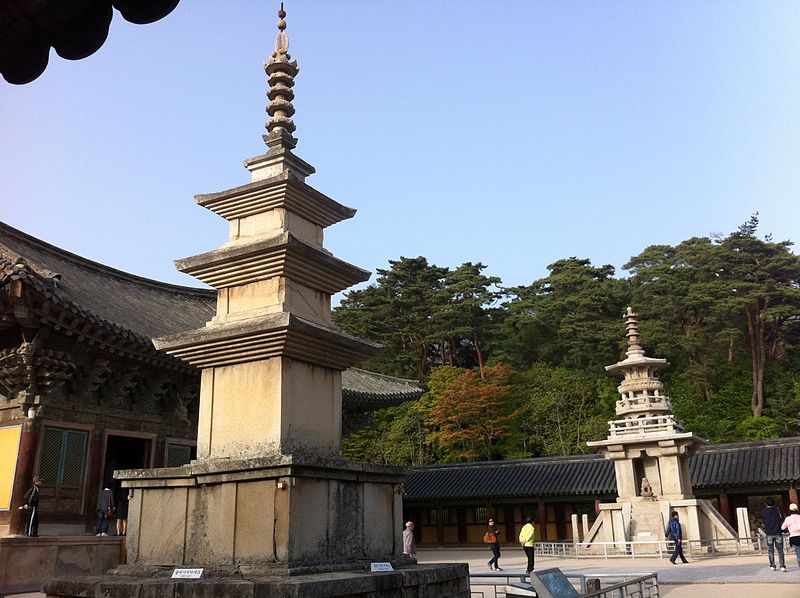
Dabotap is believed to represent the Prabhutaratna Buddha, one of the two Buddhas whose story is told in the Lotus Sutra, a key Mahayana Buddhist text. The pagoda is part of a pair with the nearby Seokgatap, which is simpler in design and represents the historical Buddha, Sakyamuni.
This historical monument not only embodies the spiritual and artistic achievements of the Silla Kingdom but also serves as an invaluable source for the study of Korean Buddhist culture. Tourists and scholars alike are drawn to Dabotap for its architectural significance and the serene beauty of its surroundings within the Bulguksa temple complex.
Dabotap – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Seokguram, Bulguksa, Seokgatap, Silla Arts and Science Museum.