Nevado del Huila

Facts and practical information
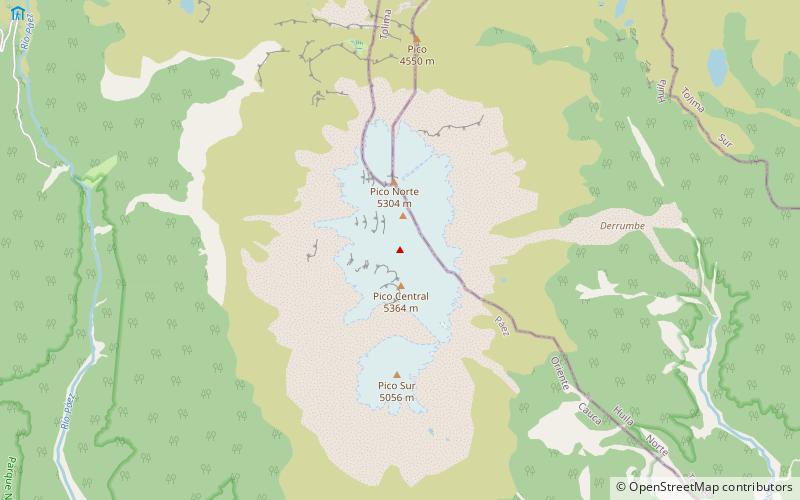
Nevado del Huila, a majestic volcano located in the Andean region of Colombia, stands as a towering beacon of nature's potent force. This stratovolcano, part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, is the highest peak in the Colombian Andes, reaching an imposing elevation of about 5,364 meters (17,598 feet) above sea level. It is not only one of the most significant natural landmarks in Colombia but also an active volcano that poses a significant geological interest to scientists and adventurers alike.
Nevado del Huila has a complex structure with multiple domes and craters due to its composite nature, resulting from successive eruptions that have layered lava, ash, and other volcanic materials. It has been the subject of monitoring and research, especially after reawakening in 2007 following a long period of dormancy. The volcanic activity prompted evacuations and remains a concern for nearby communities due to the potential for lahars—destructive mudflows caused by the melting of the glacier cap during eruptions.
The volcano is not only a geological wonder but also an ecological treasure. The surrounding region is part of Nevado del Huila National Natural Park, a protected area that spans over 1,580 square kilometers (610 square miles) and is home to diverse flora and fauna, including endangered species. The park offers a range of outdoor activities such as hiking, mountaineering, and bird watching, with the volcano itself being a challenging climb for experienced hikers due to its glaciers and unpredictable weather.
Cauca
