Thebes, Luxor

Facts and practical information
Thebes, an ancient city located in the modern city of Luxor in Egypt, stands as a testament to the grandeur of the ancient Egyptian civilization. This archaeological site, once the flourishing capital of the Pharaonic empire, is known for its monumental architecture and rich collection of tombs and temples that have survived millennia.
Thebes is divided by the Nile into the East Bank and the West Bank. The East Bank was the main living area and is home to the famous Karnak Temple Complex and Luxor Temple, while the West Bank holds the necropolis, including the Valley of the Kings and the Valley of the Queens, where pharaohs and nobility were entombed.
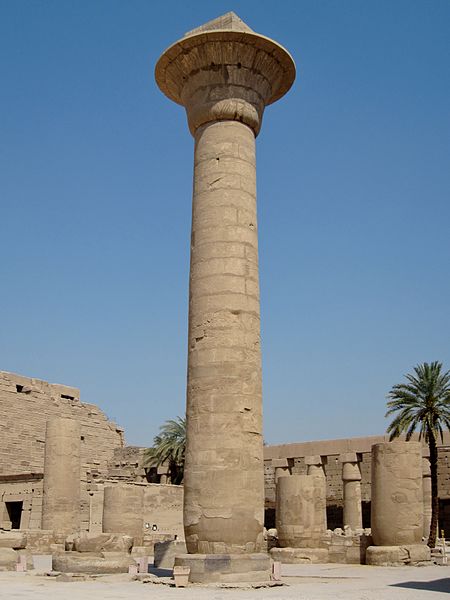
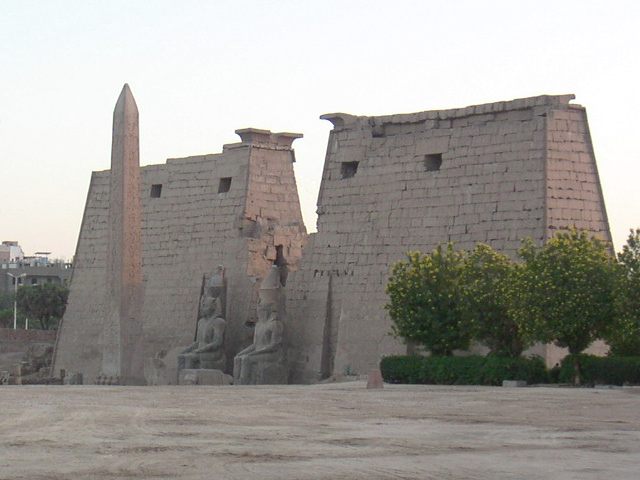
The Karnak Temple Complex is the largest religious building ever constructed, covering a vast area of land and showcasing a variety of temples, chapels, pylons, and other buildings. Its most notable structure is the Temple of Amun-Ra, adorned with massive columns and an impressive hypostyle hall. Meanwhile, the Luxor Temple, connected to Karnak by the Avenue of Sphinxes, is an elegant example of Pharaonic architecture and was dedicated to the rejuvenation of kingship.
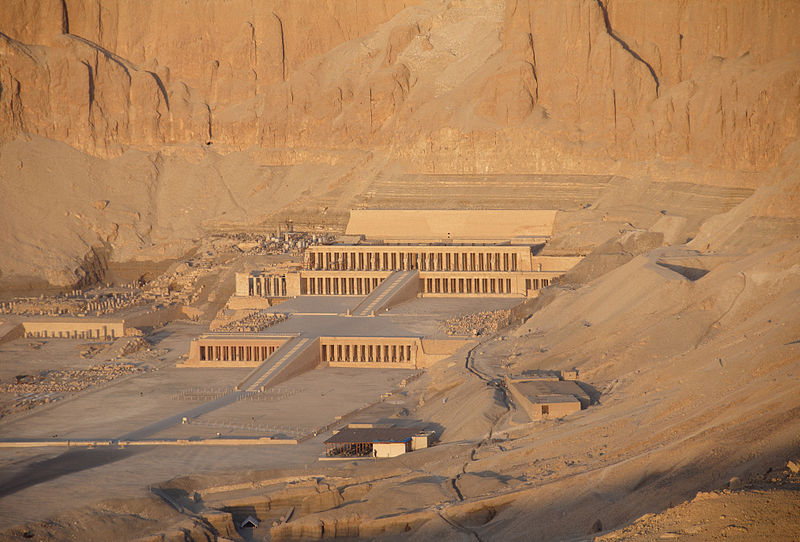
Across the Nile, the West Bank reveals a series of mortuary temples and tombs set against the backdrop of the Theban mountains. The Valley of the Kings, with its 63 royal tombs, is the final resting place of famous pharaohs such as Tutankhamun and Ramesses II. Nearby, the Valley of the Queens contains the tombs of royal consorts and offspring, including the exquisite tomb of Nefertari.
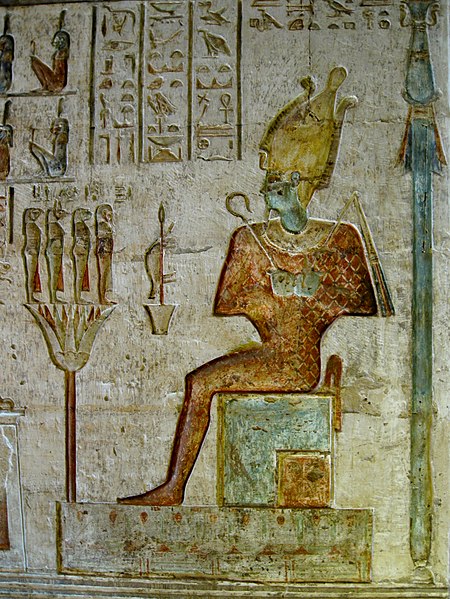
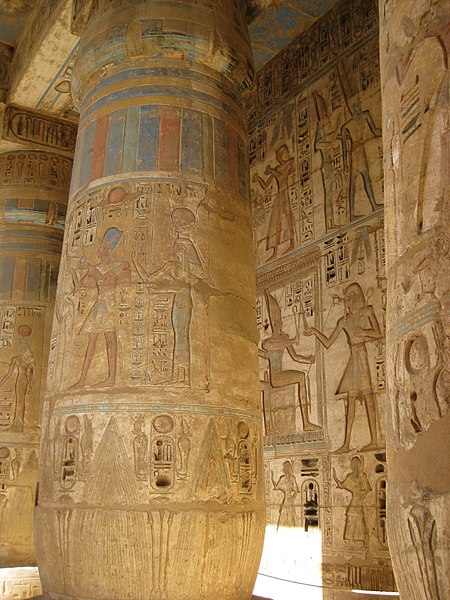
Thebes is not only a reflection of the ancient Egyptians' architectural prowess but also a repository of art, history, and culture. The wall paintings and inscriptions within the tombs provide invaluable insights into the beliefs, customs, and daily life of the ancient inhabitants.
Luxor
Thebes – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Medinet Habu, Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut, Ramesseum, Deir el-Medina.