
Zambia Travel Safety
Travel Safety in Zambia
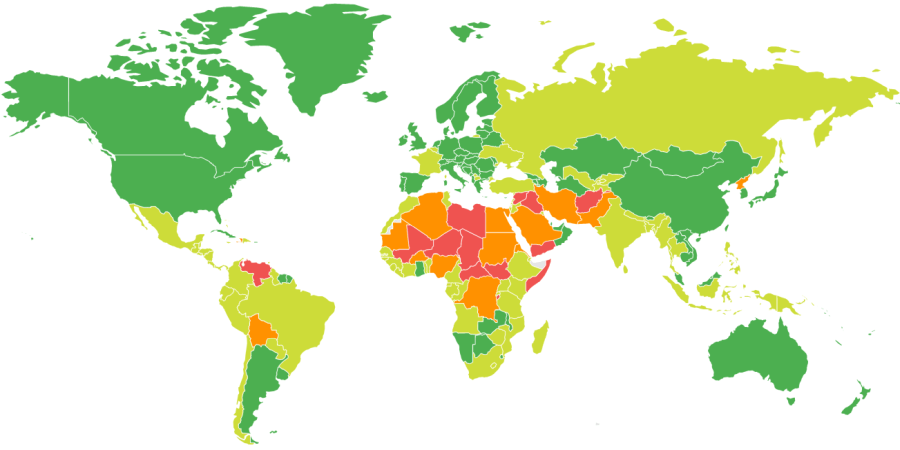
General travel safety in Zambia on a scale of 1 to 4 — where 1 is safe and 4 is dangerous. Data compiled on the basis of Canadian Department of Foreign Affairs.
Country
Zambia
Updates
Updated: 30 Jun 2025 • Still current at: 2 Jul 2025
Status
LEVEL 1 - Exercise normal safety precautions (with regional exceptions)
Use common sense and look out for suspicious behaviour. Monitor the media and other sources for changes to local travelling conditions, safety and security concerns. Laws and social customs could differ significantly. You could face terrorist attacks, civil unrest, violent crime, or unique health threats - but overall, the risks are not great.
Safety and Security Tips
Precautions
Remain alert to your surroundings and maintain a high level of personal security awareness. Avoid showing signs of affluence. If you suspect you are being followed, go directly to the closest police station or public area. Avoid walking alone after dark. Keep car doors locked and windows closed at all times. Theft often occurs at traffic chokepoints by thieves reaching through unlocked doors, open windows or unsecured cargo. Avoid using ATMs at night, have a friend to watch the area during your transaction, if possible as Thieves sometimes follow people after they withdraw money from banks or ATMs.
Road safety
Many roads are severely potholed. Traffic accidents occur frequently throughout the country, especially on Lusaka's Great East Road. Pedestrians, poorly lit and maintained vehicles, driving habits and stray animals pose risks. Avoid overland travel to rural areas after dark. As there is no nation-wide emergency service for stranded drivers, you should carry a cellular phone when travelling outside of main cities.
Taxis
Taxi fares are expensive and should be paid in local currency. Do not share taxis with strangers.
Public transportation
Exercise caution when using public transportation, especially buses, which are often overloaded.
Women's safety
Zambia is generally safe, women travelling alone should maintain personal security awareness. Women, particularly foreigners may be subject to unwanted male attention and catcalls in certain places. Be vigilant if approached by strangers seeking assistance and exercise common precautions throughout your travel.
Crime
Petty crimes such as pickpocketing, purse snatchings and vehicle break-ins are common, particularly in and around bus and railway stations, nightclubs, some shopping areas in Lusaka, Copperbelt towns, other main cities and tourist centres. Ensure personal belongings and travel documents are secure at all times. Serious crimes such as armed muggings, home invasions and sexual assault occur, particularly after dark. The use of "date rape" drugs at bars and restaurants occurs in Lusaka. Carjackings are a concern, particularly in urban areas, on the roads to and from Lusaka and on the roads in Copperbelt. Police roadblocks are common throughout the country. Police officers can request to see identity documents.
Update 1 November 2020Emergency Calls
- Police999 or 911 or 112
- Fire999 or 993 or 112
- Ambulance999 or 992 or 112
Embassy of fr
French Embassy in Lusaka
Address31F Leopard’s Hill Close
Local Law and Culture
LGBT
Homosexuality is illegal in Zambia and those caught engaging in homosexual acts can be sentenced to long terms of imprisonment and heavy fines. LGBT travellers should carefully consider traveling to Zambia.
Illegal or restricted activities
The possession or use of narcotics, including "soft" drugs such as marijuana, is strictly prohibited. Convicted offenders could face stiff penalties, including long jail sentences and/or deportation. Don't carry non-prescription medication containing diphenhydramine, such as Benadryl, as this ingredient is on the Zambian list of controlled substances. Travellers have been charged with drug trafficking and have been incarcerated. Prescription medicine should always be carried in the original container along with a copy of the prescription. Ensure that both the generic and trade names of the drug are included. A doctor's note describing why you are taking the medication is also recommended. Failure to do so could result in arrest and imprisonment. The possession of pornographic material is illegal in Zambia. Offenders may be jailed and/or deported. Ask permission before photographing individuals and photography of military installations is also prohibited.
Driving
Traffic drives on the left. An International Driving Permit is recommended. Vehicles must be equipped with two metallic emergency triangles, and white reflector stickers in front and red reflector stickers in back. Failure to comply may result in heavy fines. Turning left at a red light is prohibited. Penalties for drunk driving are severe. The use of a cell telephone while driving is prohibited.
Update 1 November 2020Vaccinations and Medications
A doctor's consultation is required prior to any vaccinations being administered. This section is for informational purposes and does not exhaust all issues related to vaccination. Please contact your doctor for complete information on this subject.
Stay Healthy and Safe
Act in advance of to prevent. Check the vaccines and medicines list and visit your doctor at least 4-8 weeks before your trip to get vaccines or medicines you may need.
All travelers
You should be up to date on routine vaccinations while traveling to any destination. Some vaccinations may also be required in Zambia.
Before each trip, it is worth making sure that we are up to date with the routine vaccinations. These include vaccinations against measles, mumps and rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, chickenpox, polio and flu.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Most travelers
Get travel vaccines and medicines because there is a risk of these diseases in the country you are visiting.
Hepatitis A is a digestive disease caused by the hepatitis A virus and is closely related to a lack of good hygiene.
It can be asymptomatic, moderate, or very severe.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Malaria is a life-threatening parasitic disease transmitted by mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Take antimalarial meds
- Prevent bug bites
Estimated relative risk of malaria in Zambia
Umiarkowane
Areas with malaria
All
Typhoid fever is an acute, systemic infectious disease caused by Salmonella typhi.
The source of the infection may include dirty water, raw fruits, vegetables, dairy products, as well as dirt containing bacteria.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Eat and drink safely
Some travelers
Vaccinations and medications that may be recommended under certain conditions, depending on where you will be, the length of your stay and the nature of your stay.
Cholera is a disease of the digestive tract caused by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
The most common infection occurs through the ingestion, mainly through water contaminated with human faeces, and also through food (mainly fruit, seafood). Less often by contact with the sick person and their environment.
Prevention
- Eat and drink safely
- Reduce your exposure to germs
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by the hepatitis B virus.
Infection occurs through contact of injured skin or mucous membranes with virus-infected blood or other secretions (e.g. during sexual contact, through contaminated needles or as a result of medical procedures).
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Avoid sharing body fluids
- Avoid non-sterile medical or cosmetic equipment
Rabies is an acute infectious disease caused by neurotrophic viruses from the rhabdovirus family.
The infection is most often caused by biting a sick animal or other contact of its saliva with mucous membranes, conjunctiva or damaged skin.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Keep away from animals
Yellow fever is an acute viral disease which is transmitted by virus-infected mosquitoes.
Prevention
- Get vaccinated
- Prevent bug bites
Vaccination requirements
Required if traveling from a country with risk of YFV transmission and ≥9 months of age, including transit >12 hours in an airport located in a country with risk of YFV transmission.
We have made every effort to ensure that the information presented reliably reflects the general safety situation in a given place. However, the data is provided for informational purposes only and we do not take responsibility for any damages or losses resulting from incorrect risk assessment. Before each trip, we recommend checking the current situation in the country of destination on the websites of the relevant Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
 Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo