Hoher Eichham

Facts and practical information
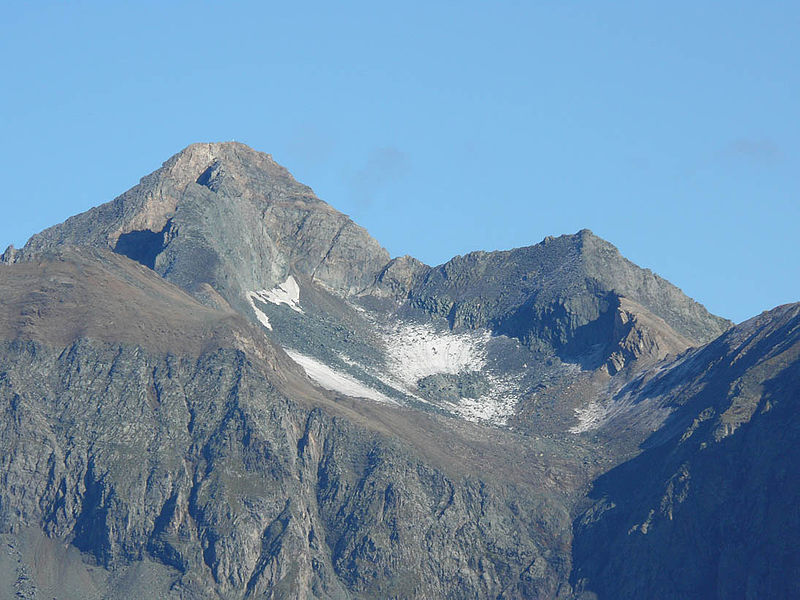
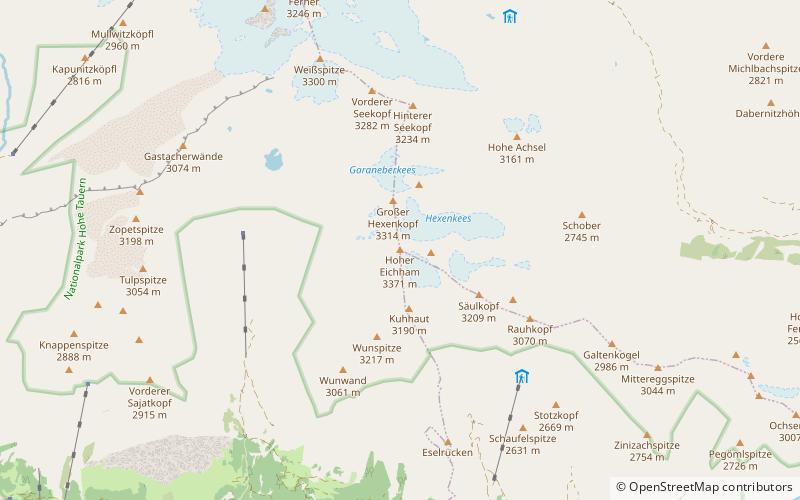
The Hoher Eichham, at 3,371 m, is the most dominant mountain in the southeastern part of the Venediger Group in the High Tauern in Austria. Four arêtes radiate from its summit towards the north, east, south and southwest. To the southeast is the glacier of Nilkees and, to the northeast, is the Hexenkees. The Großer Eichhamkees to the northwest and the Kleiner Eichhamkees to the southwest have shrunk to insignificant slabs of ice. On the North Arête is a rock tower, the Eichhamturm. Along the continuation of the arête lies the Großer Hexenkopf, which is roughly 600 metres as the crow flies from the Hoher Eichham. On the East Arête is the Niederer Eichham. From this subpeak a ridge branches southeast linking it with the Sailkopf; the lowest notch on this arête being the Sailscharte. The Hoher Eichham may have first been climbed during a military survey using triangulation in the 1850s. The first visit to the summit by tourists was on 16 July 1887 by Berlin alpinists, Carl Benzien and Hermann Meynow using the South Arête. They were led by the Zillertal mountain guide, Hans Hörhager, from Dornauberg. ()
Tyrol
Hoher Eichham – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Großvenediger, Schlatenkees, Rainerhorn, Großer Geiger.











