Facts About Rusty Forest Treefrog
Leptopelis viridis is a frog species belonging to the Arthroleptidae family, commonly found across the savannas of West and Central Africa. Its range extends from Senegal and The Gambia to the northeastern part of the Democratic Republic of Congo. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), this frog has a wide distribution across several countries in this region.
First described by Albert Günther in 1869, Leptopelis viridis has an interesting taxonomic history. In 2007, scientists confirmed that the holotype specimen initially named Leptopelis hyloides was actually the same species as Leptopelis viridis. That same year, researchers identified Leptopelis spiritusnoctis as a distinct species that inhabits forests and had previously been mistaken for Leptopelis hyloides.
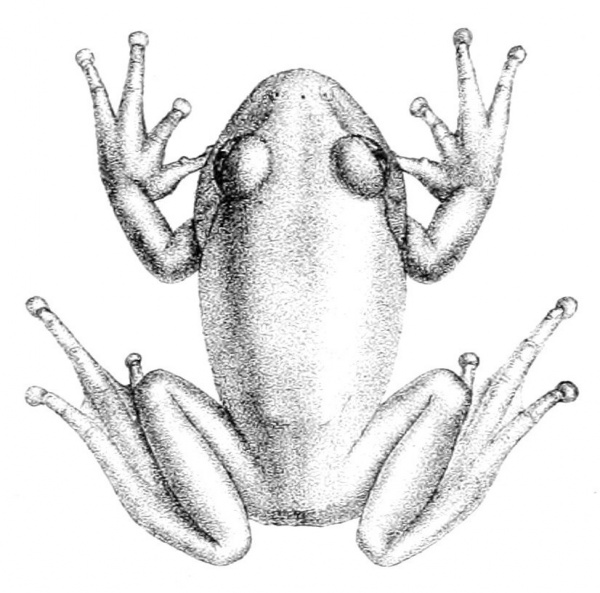
In terms of appearance, male Leptopelis viridis frogs measure about 33–35 mm in length, while females are slightly larger, at 42–48 mm. They typically exhibit a smooth brown back with darker patterns, although some individuals can appear green. These frogs breed in temporary ponds found in the savanna, laying their eggs in burrows close to water.
Habitat-wise, Leptopelis viridis thrives in both dry and humid savanna woodlands, shrublands, and grasslands. They are quite adaptable and are often found in protected areas. Currently, there are no significant threats to their population, making them a common and secure species in their natural habitat.
 Mauritania
Mauritania