Jerusalem: Archaeological Site
Places and attractions in the Archaeological site category
Categories
- Church
- Museum
- Archaeological site
- Sacred and religious sites
- Historical place
- Synagogue
- Neighbourhood
- Park
- History museum
- Temple
- Cemetery
- Shopping
- Specialty museum
- Natural attraction
- Monastery
- Mosque
- Street
- Tomb
- Memorial
- Square
- Nature
- Area
- Archaeological museum
- Art museum
- Concerts and shows
- Theater
- Architecture
- Arch
- Shopping centre
- Forts and castles
- View point
- Garden
- Valley
- Library
- Mountain
- Sport
- Sport venue
Western Wall Tunnel
The Western Wall Tunnel in Jerusalem is a remarkable archaeological site that provides an intimate glimpse into the ancient history of one of the world's most venerated cities. This subterranean passageway exposes the full length of the Western Wall, also known as the...
City of David
Nestled in the heart of Jerusalem, the City of David stands as a testament to the ancient origins of one of the world's most historically rich cities. This archaeological site is believed to be the original urban core of Jerusalem, dating back to the Bronze Age.
Pool of Bethesda
Nestled within the storied city of Jerusalem, the Pool of Bethesda stands as a testament to millennia of history, both sacred and secular. This archaeological site, once a place of healing and miracle according to Christian tradition, has attracted pilgrims...
Southern Wall
The Southern Wall is an ancient remnant of the majestic fortifications that once surrounded the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, Israel. This archaeological site is steeped in history and holds deep religious significance for Jews, Christians, and Muslims alike.
Cardo
A cardo was a north–south street in Ancient Roman cities and military camps as an integral component of city planning. The cardo maximus, or most often the cardo, was the main or central north–south-oriented street.
Pool of Siloam
The term Pool of Siloam refers to a number of rock-cut pools on the southern slope of the Wadi Hilweh, considered by some archaeologists to be the original site of Jerusalem, located outside the walls of the Old City to the southeast.
Silwan
Silwan or Siloam is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outskirts of the Old City of Jerusalem. It is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and the New Testament; in the latter it is the location of Jesus' healing the man blind from birth.
Solomon's Stables
Solomon's Stables is an underground vaulted space now used as a Muslim prayer hall by the name of El-Marwani Mosque, some 600 square yards in area, at the bottom of stairs which lead down from the al-Aqsa Mosque, under the Temple Mount, to the base of the southern wall of the Temple Mount in Jerusalem.
Ketef Hinnom
Ketef Hinnom is an archaeological site discovered in the 1970s southwest of the Old City of Jerusalem. Archaeological excavations held in the site uncovered a series of Iron Age period Judahite burial chambers, dating to the 7th and 6th centuries BCE.
Excavations
A number of archaeological excavations at the Temple Mount—a celebrated and contentious religious site in the Old City of Jerusalem—have taken place over the last 150 years.
Tomb of Benei Hezir
The Tomb of Benei Hezir, previously known as the Tomb of Saint James, is the oldest of four monumental rock-cut tombs that stand in the Kidron Valley, adjacent to the Tomb of Zechariah and a few meters from the Tomb of Absalom.
Acra
The Acra is both the name of a fortified structure and also one of three residential areas in Jerusalem during the late Second Temple period from which it takes its name.
Sultan's Pool
The Sultan's Pool is an ancient water basin to the west side of Mount Zion, Jerusalem. The Sultan's Pool was part of the water supply network for Jerusalem from the late Second Temple period to the late Ottoman period.
Givati Parking Lot dig
Givati Parking Lot dig is an archaeological excavation located in the Tyropoeon Valley. It is adjacent to the City of David, the most ancient part of the Canaanite and Israelite city of Jerusalem.
Hezekiah's Pool
Hezekiah's Pool, or the Patriarch's Pool, located in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem, was once a reservoir forming part of the city's ancient water system.
Silwan necropolis
The Silwan necropolis is the most important cemetery in ancient Judea, and is assumed to have been used by the highest-ranking officials residing in Jerusalem. Its tombs were cut between the 9th and 7th centuries BCE.
Tombs of the Sanhedrin
Tombs of the Sanhedrin, also Tombs of the Judges, is an underground complex of 63 rock-cut tombs located in a public park in the northern Jerusalem neighborhood of Sanhedria.
Mamilla Pool
Mamilla Pool is one of several ancient reservoirs that supplied water to the inhabitants of the Jerusalem. It is located outside the walls of the Old City about 650 metres northwest of Jaffa Gate in the centre of the Mamilla Cemetery.
Temple Mount Sifting Project
The Temple Mount Sifting Project is an archaeological project begun in 2004 whose aim is the recovery and study of archaeological artifacts contained within debris which was removed from the Temple Mount in Jerusalem without proper archaeological care.
Monolith of Silwan
The Monolith of Silwan, also known as the Tomb of Pharaoh's Daughter, is a cuboid rock-cut tomb located in Silwan, Jerusalem dating from the period of the Kingdom of Judah; the latter name refers to a 19th-century hypothesis that the tomb was built by Solomon for his Egyptian wife.
Tombs of the Kings
The Tombs of the Kings are a rock-cut funerary complex in East Jerusalem believed to be the burial site of Queen Helene of Adiabene, hence: Helena's Monuments.
Struthion Pool
The Struthion Pool, effectually translated from the Greek as 'Sparrow Pool' is a large cuboid cistern beneath the Convent of the Sisters of Zion in the Old City of Jerusalem, built by Herod the Great in the first century BCE.
Givat HaMivtar
Givat HaMivtar is an Israeli settlement and a neighborhood in East Jerusalem established in 1970 between Ramat Eshkol and French Hill. It is located on a hill where an important battle took place in the Six Day War. Archaeological excavations have revealed important ancient Jewish tombs in the region.
Cave of the Minor Sanhedrin
The Cave of the Minor Sanhedrin is a burial cave located next to the Tomb of Simeon the Just in the Sheikh Jarrah neighborhood of Jerusalem. It contains 26 burial niches, in which the 26 members of the Minor Sanhedrin are said to be buried. There are also other burial caves in the complex.
Tabachnik Garden
Tabachnik National Garden is a National Park located on the southern slopes of Mount Scopus in Jerusalem, next to the Hebrew University. The garden preserves some Jewish burial caves from the Second Temple period and two small modern cemeteries, the American Colony Cemetery and the Bentwich Cemetery.
Birket Israel
Birket Israel also Birket Israil or Birket Isra'in, abbreviated from Birket Beni Israìl was a public cistern located on the north-eastern corner of the Temple Mount, in Jerusalem.
Betar Fortress
Betar, also spelled Beitar or Bethar, was an ancient fortified Jewish village in the Judean Mountains. It was the last standing stronghold of the Bar Kokhba revolt, and was destroyed by the Imperial Roman Army under Hadrian in 135 CE.
Cave of the Ramban
The Cave of the Ramban is located in the southern cliff of the Upper Kidron Valley, on a slope descending into the Arab neighborhood of Wadi al-Joz, Jerusalem.
Israelite Tower
The Israelite Tower is an archaeological site in Jerusalem's Jewish Quarter. The site features remains of the city's Iron Age fortifications which were later incorporated into the Hasmonean city walls. It was excavated by Israeli archaeologist Nahman Avigad during the 1970s.
Huldah Gates
The Huldah Gates were one of the Gates of the Old City of Jerusalem leading into the Jerusalem Temple compound in the Hasmonean period and were named as such in the Mishnah.
Pool of Gibeon
The Pool of Gibeon is a site in Gibeon mentioned a number of times in the Hebrew Bible. Archeological evidence locates the historical site of the pool in the village of Jib, in the West Bank Palestinian territories.
Finger of Og
The Finger of Og King of Bashan, is the name given to a huge stone pillar, sometimes called Herod's Pillar, which lies in front of the Russian Compound in Jerusalem.
Gibeon Ancient City
Gibeon was a Canaanite and Israelite city north of Jerusalem. According to Joshua 10:12 and Joshua 11:19, the pre-conquest inhabitants of Gibeon, the Gibeonites, were Hivites; according to 2 Samuel 21:2 they were Amorites.
Tower of David
The Tower of David is the northeast tower of the Citadel of Jerusalem. It has been identified as either the Phasael Tower or the Hippicus Tower described by Josephus.
Qubur Bani Isra'il
Qubur Bene Isra'in or Qubur Bani Isra'il, are four, formerly five, huge stone structures dated to the Middle Bronze Age, which rise from a rocky plateau overlooking Wadi Qelt in the West Bank, about 3.5 miles northeast of Jerusalem, between Hizma and Geva Binyamin along Highway 437.
Antonia Fortress
The Antonia Fortress was a citadel built by Herod the Great and named for Herod's patron Mark Antony, as a fortress whose chief function was to protect the Second Temple.
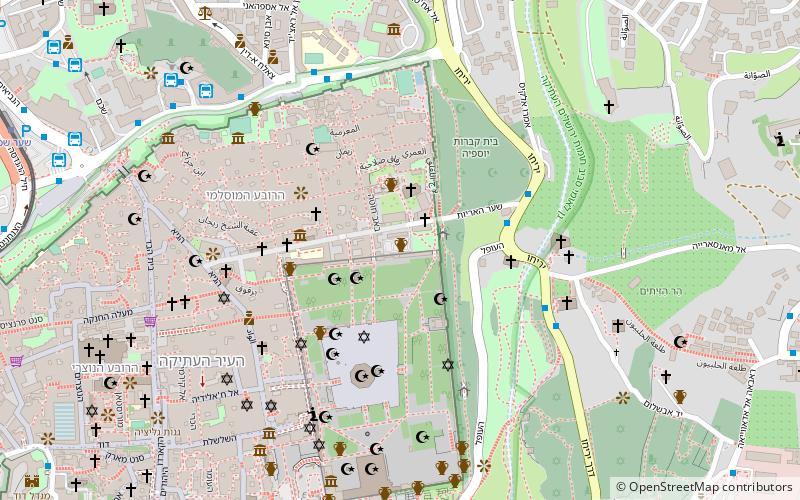
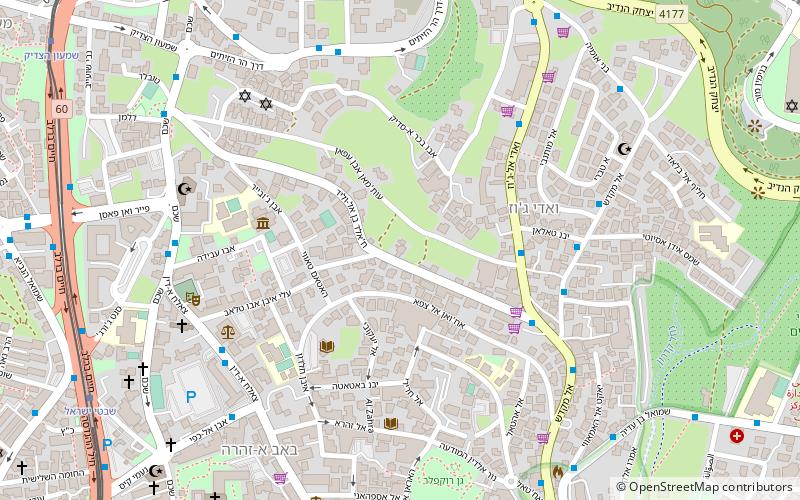
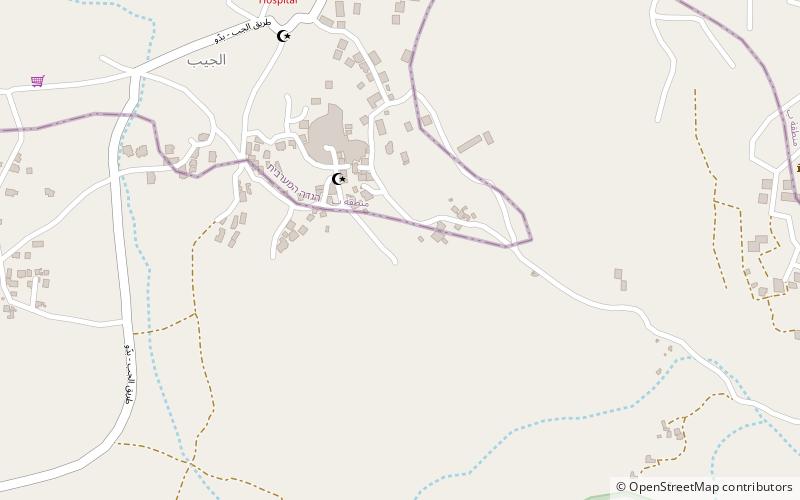
Map