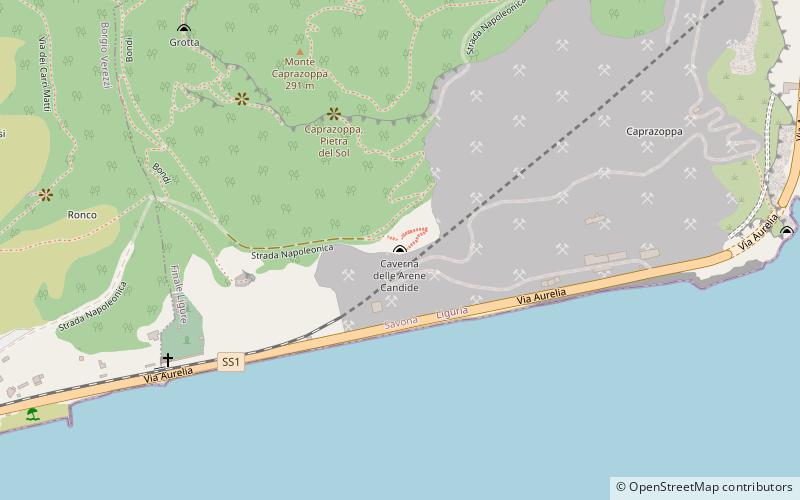
Arene Candide

Facts and practical information
Nestled on the Ligurian coast of Italy, the Arene Candide cave is a prehistoric site that offers a unique glimpse into the lives of early humans. This natural cavern, known for its rich archaeological significance, has been a focal point for researchers interested in understanding the cultural and ritual practices of ancient communities.
The cave itself is a vast and intricate space, with evidence of human occupation dating back to the Upper Paleolithic era. It was first excavated in the 1940s, and since then, a wealth of artifacts, including tools, ornaments, and human remains, have been uncovered. These finds have provided invaluable insights into the ways our ancestors lived, worked, and honored their dead.
One of the most notable discoveries within Arene Candide is the so-called "Young Prince" burial. This grave, believed to be around 25,000 years old, contained the remains of a young man adorned with a wealth of grave goods, such as shell necklaces, flint tools, and ochre, suggesting a complex social structure and ritualistic burial practices.
The cave's interior reveals a record of continuous human activity, with layers of occupation that chronicle the transition from hunter-gatherer societies to early agricultural communities. The presence of art and symbolism, including wall engravings and personal ornaments, speaks to the cognitive and artistic development of the cave's ancient inhabitants.
Arene Candide – popular in the area (distance from the attraction)
Nearby attractions include: Borgio Verezzi Caves, Duomo di San Giovanni Battista, Church of San Biagio, Final Pia.








